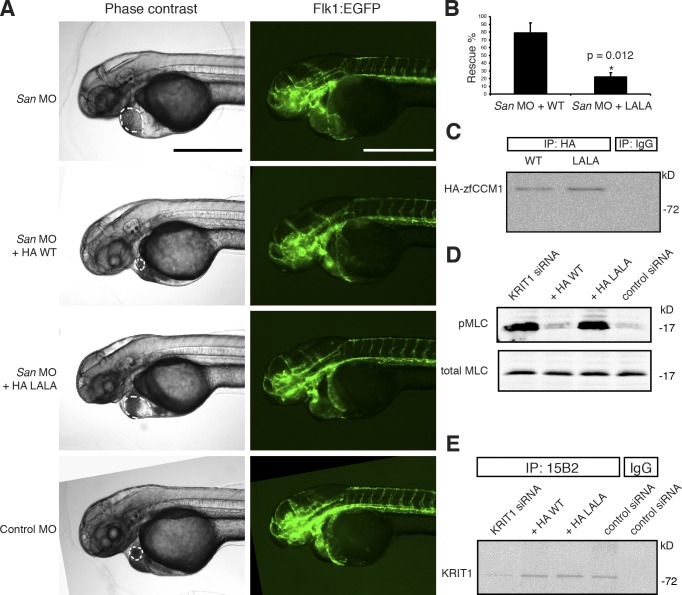
Figure 5.
KRIT1–HEG1 interaction is required for normal zebrafish cardiovascular development and inhibition of RhoA/Rho kinase in EC. (A) Flk1:EGFP transgenic krit1-morphant (San MO) embryo showed enlarged heart phenotype. Coinjecting the cRNA encoding HA-tagged wild-type (WT) zebrafish krit1 protein reduced the heart size of injected fish, whereas fish coinjected with cRNA encoding HA-tagged Krit1 (L714,L718A), orthologous to human KRIT1(L717,L721A) mutant still exhibited a dilated heart phenotype. Dilated heart phenotype was scored by cardiac dilation in living fish. Authentic dilation was verified by indentifying the endocardium in the fluorescence images, which is indicated by the dotted lines. All microscopic images were taken at 48 hpf. Bars, 500 µm. (B) Bar graphs showing effects of Krit1 (L714,718A) mutant on zebrafish cardiovascular development. Data are expressed as number of embryos without dilated heart phenotype divided by total number of embryos used per experiment × 100; means ± SD. *, P < 0.05 compared with San MO + HA-WT cRNA group. Data are from three independent experiments. Total number of animals used: 94 in San MO + HA-WT group and 71 in San MO + HA-Krit1(L714,718A) group. (C) Both HA-tagged zebrafish Krit1 WT and Krit1(L714,718A) proteins were expressed at similar levels in injected embryos as revealed by immunoprecipitation with a rabbit anti-HA antibody from zebrafish embryo lysates and immunoblotting with a mouse anti-HA antibody. (D) Effect of disruption of the HEG1–KRIT1 interaction on RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in EC. Silencing of KRIT1 caused a marked increase in myosin light chain phosphorylation that was not reversed by expression of KRIT1 (L717,721A). (E) Extent of KRIT1 depletion and reconstitution in the experiment depicted in D. IP, immunoprecipitation; LALA, KRIT1(L717A,L721A); MLC myosin light chain.