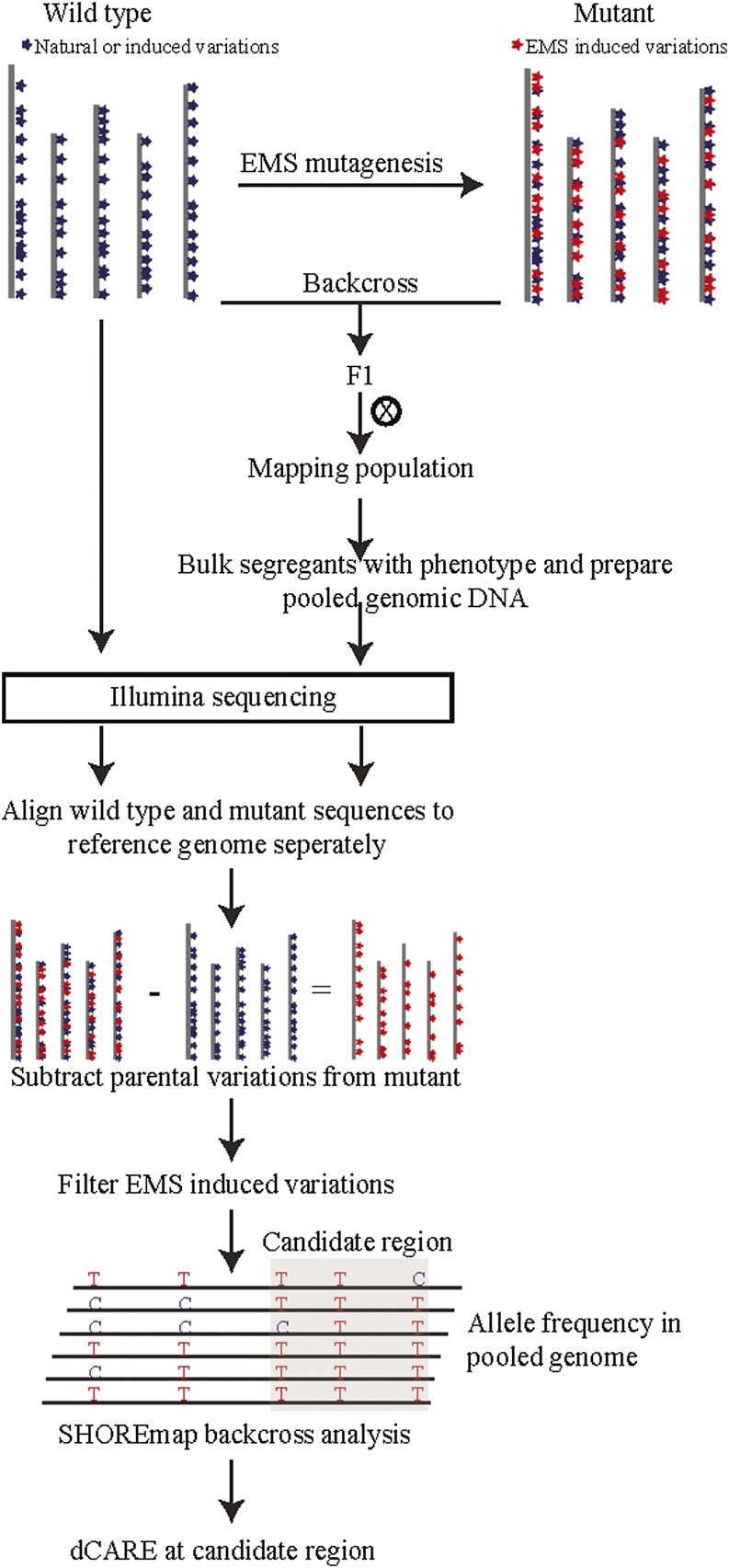
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the fast isogenic mapping approach. Chemical mutagens typically introduce hundreds of novel mutations. Within the M2 generation, mutants are screened for phenotypes. Selected plants are backcrossed to the nonmutagenized progenitor. The F2 offspring of such a cross forms an isogenic mapping population, as only novel mutations are segregating. Backcrossed individuals that display the mutant phenotype are selected, bulked, and their DNA is prepared as a pool and whole-genome sequenced. If the parental line is genetically different from the reference line Col-0, it needs to be resequenced in order to control for naturally occurring differences that need to be differentiated from novel mutations. Thus, all novel EMS-induced mutations can be selected for SHOREmap analysis by filtering for mutations that do not reside in the parental line. Candidate mutations (gray box) that show high mutant allele frequencies and linkage are selected for dCARE to pinpoint the causal mutation.