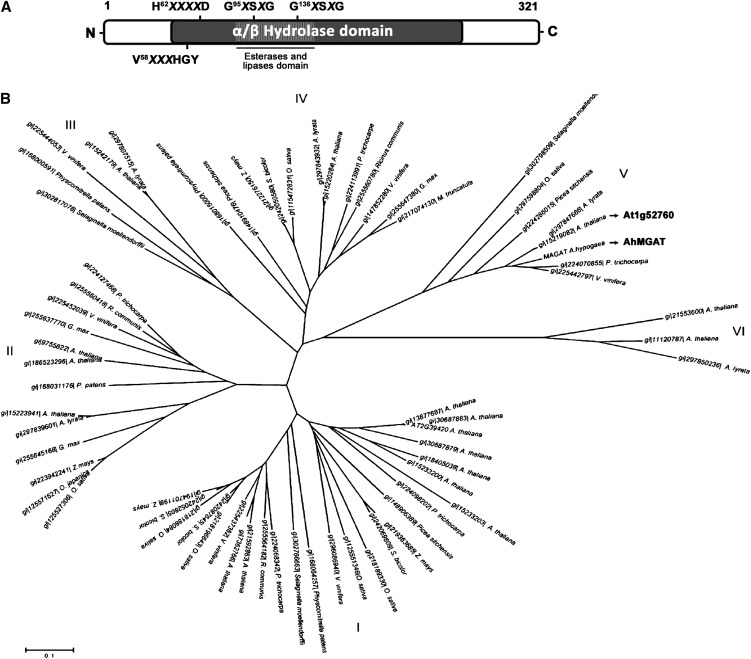
Figure 1.
The domain structure and phylogenetic analysis of peanut MGAT. A, Schematic representation of domains retrieved from the conserved domain database at the NCBI: α/β-hydrolase fold (COG0596 and COG1073); PldB, lysophospholipase (COG2267); esterase (COG1647). The presence of an acyltransferase motif (H62X4D) and two lipase motifs (G95XSXG and G136XSXG) are indicated. B, Phylogenetic tree of AhMGAT and its homologs in plants. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method with 500 replicates. The length of the branches is proportional to the degree of divergence and, thus, corresponds to the statistical significance of the phylogeny between the protein sequences. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method; units used were number of amino acid substitutions per site. All positions with gaps and missing data were eliminated from the data set (complete deletion option). A phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA4.