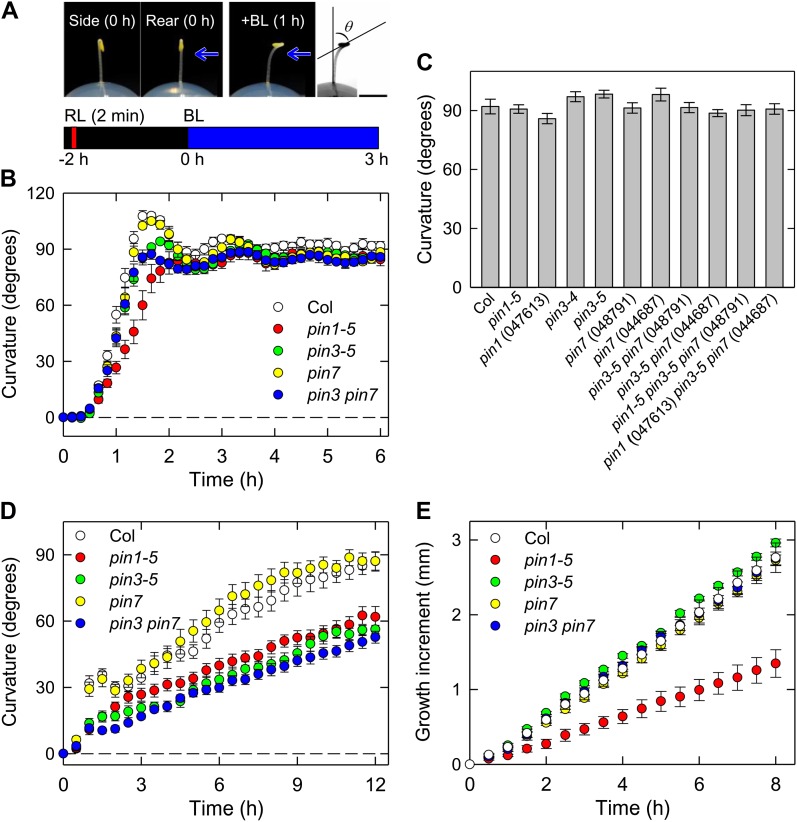
Figure 1.
Phototropism, gravitropism, and elongation growth in Arabidopsis hypocotyls. A, Illustration of the experimental procedures used to evaluate hypocotyl phototropism. Representative pictures of the shoot of a dark-grown Arabidopsis seedling are shown on the top. The left (side view) and middle (rear view) images are of a 2-d-old dark-grown seedling prior to phototropic induction. The seedling was pretreated with overhead red light (RL) at 20 μmol m−2 s−1 for 2 min. After 2 h, the hypocotyl was irradiated with blue light (BL) at 0.17 μmol m−2 s−1 perpendicularly to the hook plane to induce phototropic curvature. The representative picture shown on the right was taken 1 h after the onset of blue light. Black bar, 2 mm. The bottom shows the experimental scheme used to analyze phototropism. B, Time course analyses of hypocotyl phototropism. The etiolated seedlings were pretreated with overhead red light at 20 μmol m−2 s−1 for 2 min, and after 2 h, they were stimulated continuously with unilateral blue light at 0.17 μmol m−2 s−1. Phototropic curvatures were determined at 10-min intervals. The pin1-5, pin3-5, and pin7 (Salk_048791) single mutants, and the pin3 pin7 double mutant were used. The data shown are the means ± se from nine to 10 seedlings. C, Hypocotyl phototropism of pin mutants. The hypocotyls of pin single, double, and triple mutants were stimulated with unilateral blue light, and the hypocotyl curvatures were determined 3 h after the onset of blue light. The data shown are the means ± se from 10 to 19 seedlings. D, Time courses of hypocotyl gravitropism. The etiolated seedlings were displaced by 90°. Gravitropic curvatures were determined at 30-min intervals. The data shown are the means ± se from 10 to 22 seedlings. E, Time course analysis of the elongation growth of hypocotyls. The hypocotyl lengths were determined at 30 min intervals for 8 h. The data shown are the means ± se from eight to 10 seedlings.