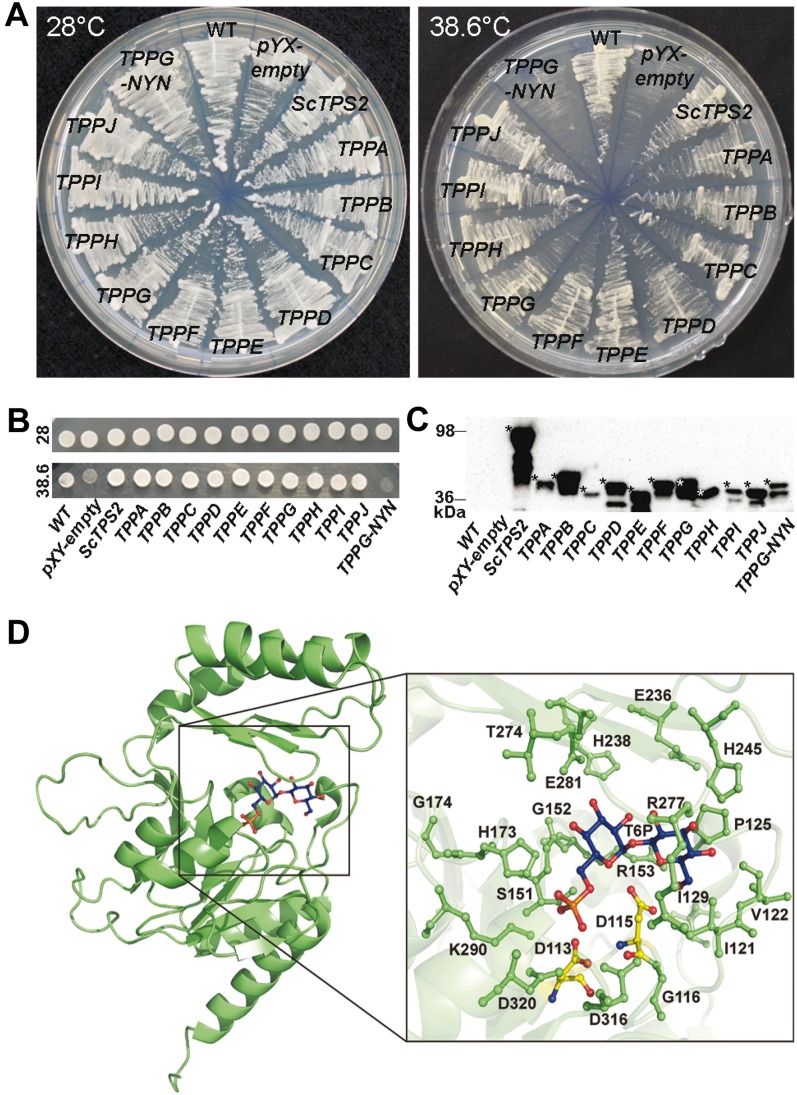
Figure 2.
The 10 Arabidopsis TPP candidates display heterologous TPP activity. A, Yeast tps2Δ growth complementation assay of TPP Arabidopsis proteins at 38.6°C with strains grown at a permissive temperature of 28°C as control treatment. tps2Δ yeast strains expressing the TPPG-NYN mutant (Asp-113 and Asp-115 of wild-type TPPG were mutated to Asn) showed heat-sensitive growth phenotype, indicating the double mutation causes loss of TPPG catalytic activity. B, For the spot assay, cells of all samples were diluted to OD600 1 and incubated at 28°C and 38.6°C. C, Expression of the HA-tagged proteins was confirmed by western-blot analysis. Asterisks indicate the full-length tagged protein, based on the predicted mass (The Arabidopsis Information Resource) and the prestained protein standard. D, Overall representation model of the TPPG protein (green), and detail of T6P (blue) modeled in the active site of TPPG. Catalytic important residues near the active site are reported in green ball and stick figures. The two Asp of motif I, which are predicted to play a crucial role in the substrate binding and the catalytic mechanism, are indicated in yellow. Asp-113 and Asp-115 of TPPG (TPPG wild type) were mutated to Asn (TPPG-NYN). Figures prepared with PYMOL (DeLano, 2002).