Figure 4.
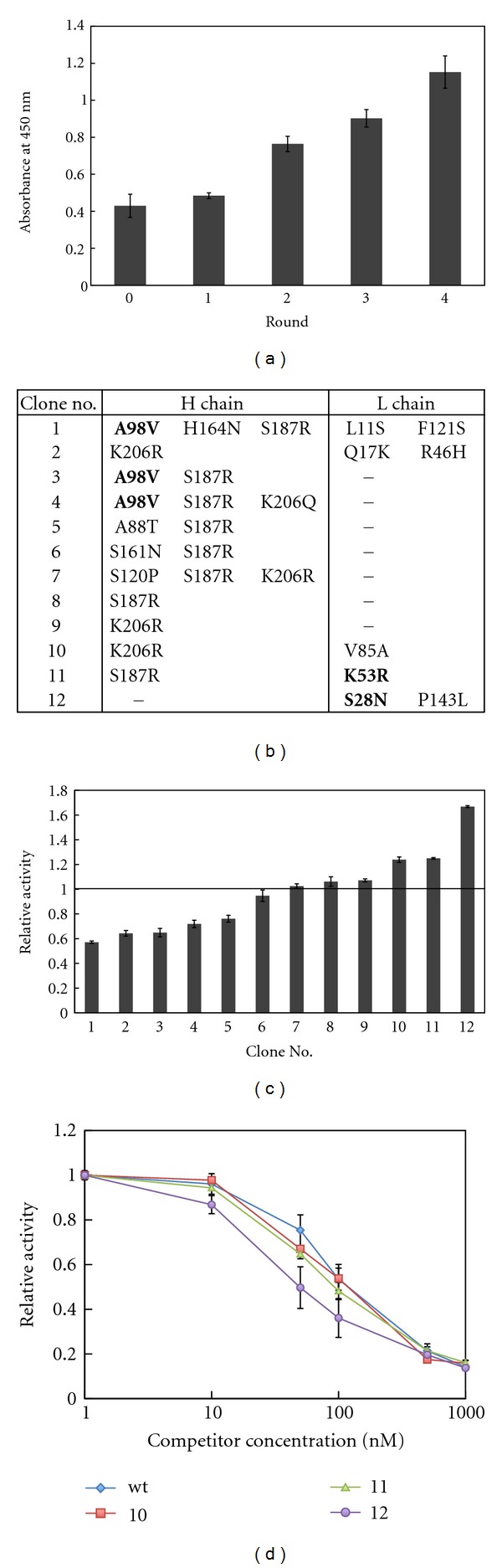
Affinity selection of randomly mutated anti-p53 Fab fragments. (a) Binding activity of the library after each round of selection. Random mutations were introduced to anti-p53 Fab fragments and 4 rounds of affinity selection were carried out under decreasing antigen concentration (round 1, 400 nM; round 2, 40 nM; round 3, 4 nM; round 4, 0.4 nM). After each round of selection, the fraction of the mutant Fab fragment library that binds to p53 was monitored by ELISA. Round 0 represents the randomly mutated initial library before selection. (b) Amino acid mutations of the selected variants. Bold type represents the mutations in the CDR and the minus (−) represents no amino acid mutations. (c) Binding activity of the selected variants after the 4th round of selection. The antigen binding activities of the selected variants were measured by ELISA. The absorbance at 450 nm of the wild type was used for normalization. (d) Competitive ELISA for estimating their affinities of variants with higher binding activity than the wild type. Competitive ELISA was preformed with 0–1000 nM free p53 for clone number 10–12 and the wild type (wt). The signals were normalized to that of 0 nM competitor concentration.
