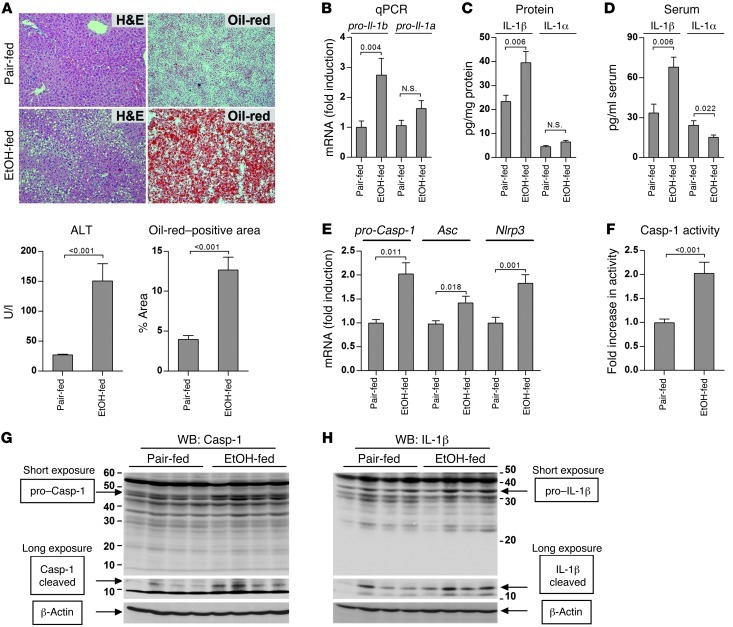
Figure 1. Activation of the inflammasome and IL-1β in alcohol-induced liver injury.
WT mice were fed control (pair-fed) or alcohol (EtOH-fed) diet and sacrificed 4 weeks later. Liver samples were stained by H&E or Oil-red-O, and liver injury and steatosis was quantified by measuring serum ALT and Oil-red-O–positive areas, respectively (A). Expression of pro–IL-1β and pro–IL-1α in the liver was analyzed by qPCR (B) and ELISA (C). Secreted forms of IL-1β and IL-1α were measured in the serum using specific ELISA (D). Expression of pro-Casp-1, Asc, and Nlrp3 in the liver was measured using qPCR (E), and Casp-1 activity was measured using a colorimetric assay (F). Cleaved forms of Casp-1 (G) and IL-1β (H) in the livers were analyzed using antibodies that identify both full-length pro-form (short exposure, presented in linear contrast mode) and cleaved forms (long exposure, presented in sigmoidal contrast mode), and normalized to β-actin. See Supplemental Figure 1 for densitometric analysis. n = 5 (pair-fed); 10 (EtOH-fed). Numbers in graphs denote P values. Original magnification, ×200.