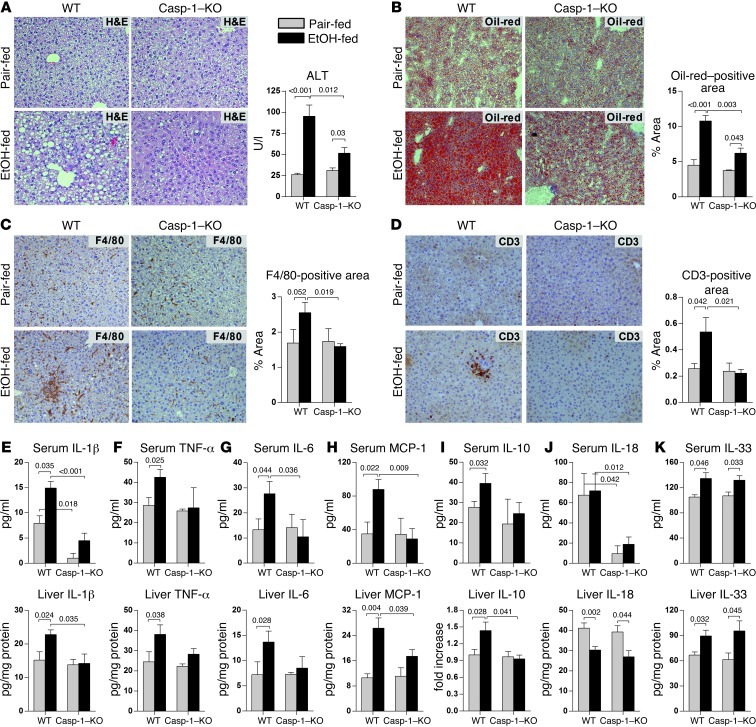
Figure 2. Deficiency of Casp-1 attenuates alcoholic liver inflammation, steatosis, and damage.
WT or Casp-1–KO mice were fed control or alcohol diet and sacrificed 4 weeks later. Liver injury was assessed by liver H&E staining and serum ALT (A). Steatosis was evaluated by Oil-red-O staining (B). Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate recruitment of F4/80-positive macrophages (C) and CD3-positive lymphocytes (D). Serum and liver levels of IL-1β (E), TNF-α (F), IL-6 (G), MCP-1 (H), IL-10 (I), IL-18 (J), and IL-33 (K) were measured as described in Methods. Tissue levels of IL-10 (I; liver) were evaluated using immunoblotting (Supplemental Figure 3A). n = 6 (WT pair-fed); 11 (WT EtOH-fed); 3 (Casp-1–KO pair-fed); 7 (Casp-1–KO EtOH-fed). Numbers in graphs denote P values. Original magnification, ×200.