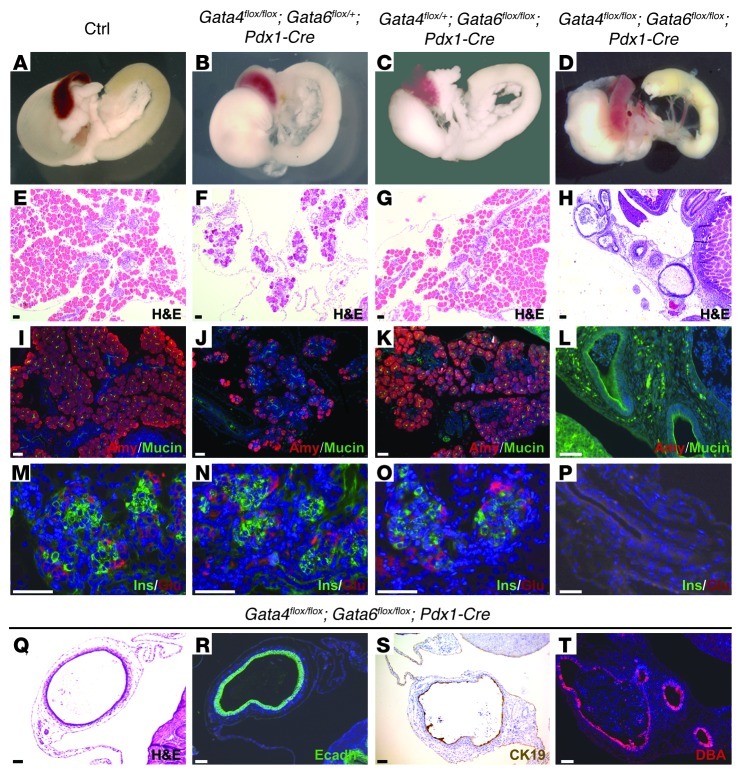
Figure 2. Pancreatic agenesis in Gata4/Gata6 double mutant.
Gross appearance of neonatal WT and conditional mutant guts (A–D) and pancreatic sections stained with H&E (E–H) reveal the abnormal morphology of double-mutant pancreata at P1. Gata4flox/flox;Gata6flox/+;Pdx1-Cre mice show pancreatic hypoplasia with scarcity of acinar cells (B and F). Gata4flox/+;Gata6flox/flox;Pdx1-Cre mice display normal pancreatic mass and architecture (C and G). Immunohistochemical analysis shows reduced expression of the acinar marker, amylase, in Gata4flox/flox;Gata6flox/+;Pdx1-Cre pancreatic sections (J) compared with Gata4flox/+;Gata6flox/flox;Pdx1-Cre (K) and control littermates (I). The double-mutant pancreatic remnant displays cystic structures surrounded by abundant stroma (H, L, P, and Q). The cystic structures express mucin (L) and cytokeratin 19 (S) and react with DBA lectin (T), which are markers of differentiated ductal cells. Immunostaining for E-cadherin confirms the epithelial nature of the cysts (R). Insulin and glucagon staining reveals normal differentiation of the endocrine lineage in Gata4flox/flox;Gata6flox/+;Pdx1-Cre (N) and Gata4flox/+;Gata6flox/flox;Pdx1-Cre (O) mutant mice in comparison with control mice (M). In contrast, Gata4/Gata6 double-mutant mice lack endocrine cells (P). Counterstaining with DAPI was performed to reveal nuclei. Scale bars: 50 μm.