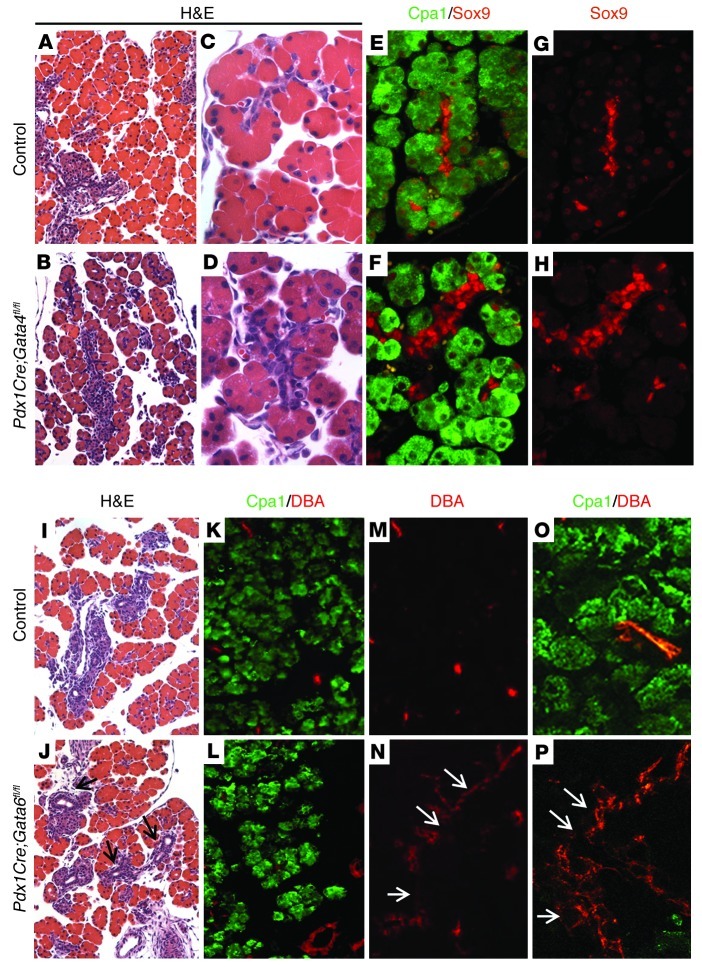
Figure 1. Pancreas-specific deletion of either Gata4 or Gata6 causes mild embryonic pancreas defects.
(A–D) H&E staining of representative sections of E18.5 dorsal pancreas from control Gata4fl/fl (A and C) and Pdx1Cre;Gata4fl/fl embryos (B and D). (E–H) Immunofluorescence staining for Sox9 (red) and Cpa1 (green) of E18.5 dorsal pancreas from control Gata4fl/fl (E and G) and Pdx1Cre;Gata4fl/fl embryos (F and H). Cpa1 is expressed in acinar cells (E and F). Sox9 is expressed in ductal cells and centroacinar cells in both control and Pdx1Cre;Gata4fl/fl embryos (E and F). In acinar cells, Sox9 is expressed in control pancreas (G), but is absent in most Gata4-depleted acinar cells of Pdx1Cre;Gata4fl/fl pancreas (H). Original magnification, ×200 (A and B); ×640 (C–H). (I and J) H&E staining of representative sections of E18.5 control Gata6fl/+ (I) and Pdx1Cre;Gata6fl/fl (J) embryos. (K–P) Immunofluorescence staining of E18.5 control Gata6fl/+; R26R-LacZ (K, M, and O) and Pdx1Cre;Gata6fl/fl (L, N, and P) embryos. Cpa1 (green) expression is in the acinar cells, and DBA (red) marks the epithelial ductal regions. Increased ductal tissues are observed in Pdx1Cre;Gata6fl/fl pancreas (arrows in J, N, and P). Original magnification, ×200 (I–N); ×640 (O and P).