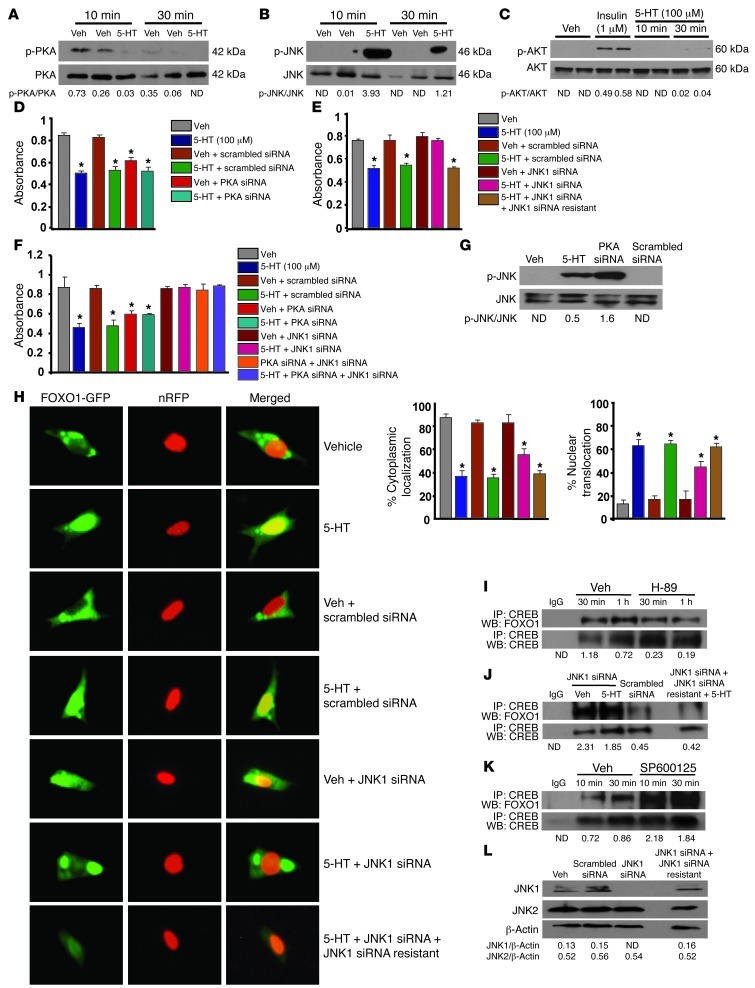
Figure 6. PKA/JNK1-dependent signaling localizes FOXO1 to the nucleus.
Immunoblot showing (A) PKA, (B) JNK1, and (C) AKT phosphorylation in OB-6 cells treated with serotonin (100 μM). (D and E) Proliferation in primary osteoblasts transfected with (D) PKA siRNA oligos or control scrambled siRNA oligos or (E) JNK1 siRNA or control scrambled siRNA oligos, in the presence or absence of siRNA-resistant JNK1, followed by treatment with vehicle or serotonin (100 μM) for 48 hours (n = 3). (F) Proliferation in primary osteoblasts transfected with indicated siRNAs or control scrambled siRNA oligos, followed by treatment with vehicle or serotonin (100 μM) for 48 hours (n = 3). (D–F) *P < 0.05 versus vehicle. (G) Immunoblot of JNK1 phosphorylation in OB-6 cells transfected with PKA siRNA and control scrambled siRNA oligos. (H) Subcellular localization of Foxo1 in primary osteoblasts transfected with JNK1 siRNA oligos or control scrambled siRNA oligos, followed by cotransfection with FOXO1-GFP and nRFP plasmids, in the presence or absence of siRNA-resistant JNK1. Transfected cells were treated with serotonin (100 μM) for 6 hours. Subcellular localization of FOXO1 was expressed as the percentage cytoplasmic or nuclear localization (n = 3). Original magnification, ×4. *P < 0.05 versus vehicle. (I–K) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting of CREB and FOXO1 in OB-6 cells (I) treated with PKA inhibitor (H-89) or (J) transfected with JNK1 siRNA, with or without siRNA-resistant JNK1 or control scrambled siRNA oligos, or (K) treated with the JNK inhibitor SP600125 at 10 μM. (L) Immunoblotting for JNK1 and JNK2 protein levels in OB-6 cells. Blots were representative of 3 experiments.