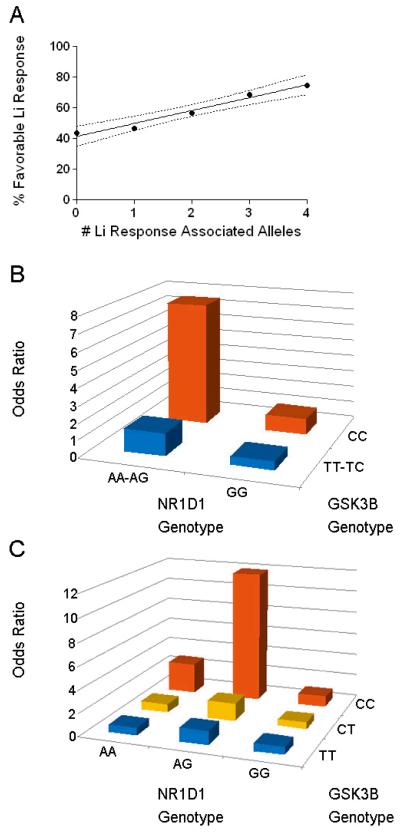
Figure 1.
Additive effects of GSK3β and NR1D1 alleles on lithium response. A) All possible genotype combinations at rs2071427 and rs6438552 were determined for all Li-R and Li-NR subjects and scored (0-4) for the number of alleles associated with favorable lithium outcomes. Dashed lines indicate 95% confidence intervals for the regression line. Rates of response for each allelic combination are the following: 4 alleles: 75% (N=4), 3 alleles: 69% (N=26), 2 alleles: 57% (N=95), 1 allele: 44% (N=108), 0 alleles: 47% (N=48). B) Odds ratios for lithium response calculated for each of 2×2 GSK3β and NR1D1 genotype combinations using dominant and recessive models. Sample sizes for each subgroup are as follows: AA-AG:CC N=17, AA-AG:TT-TC N=116, GG:TT-TC N=119, GG:CC N= 29 C) Odds ratios for lithium response calculated for each of 3×3 GSK3β and NR1D1 genotype combinations. Sample sizes for each subgroup are as follows: AA:CC N=4, AA:TC N=13, AA:TT N=7, AG:CC N=13, AG:TC N=59, AG:TT N=37, GG:CC N=29, GG:TC N=71, GG:TT N=48.