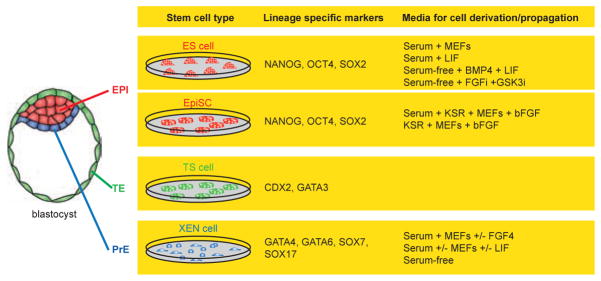
Fig. 4. Stem cells that can be derived from blastocyst stage mouse embryos.
Three stem cells can be isolated from a mouse blastocyst embryo. Embryonic stem (ES) cells and Epi stem cells (EpiSCs) from the epiblast (red), trophoblast stem (TS) cells from the trophectoderm (green) and extraembryonic endoderm (XEN) cells from the primitive endoderm (blue). These stem cells are characterized by their distinct morphologies, their developmental potential in chimeras, as well as the expression of different sets of lineage-specific transcription factors (the transcription factors listed can be recognized by commercially available antibodies) and by the conditions used to isolate and propagate them in culture.