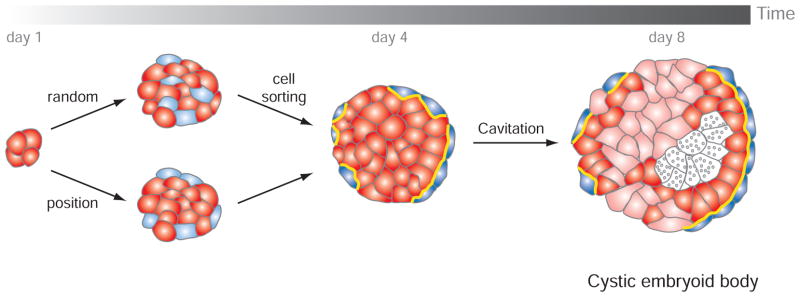
Fig. 5. Schematic representation of the first differentiation events occurring in an embryoid body.
An initial morphological event is the formation of an outer layer of extraembryonic endoderm cells (blue). This could be the result from the random differentiation of ES cells (red) within the embryoid body and subsequent cell sorting, and/or from the differentiation of cells residing at the periphery and exposed to the outside environment. Extraembryonic endoderm cells secrete ECM components that will participate in the maturation of an epithelial epiblast and in the cavitation (grey dots indicate cell death). This process is usually not homogenous within an embryoid body and is accompanied by cell differentiation (pink cells).