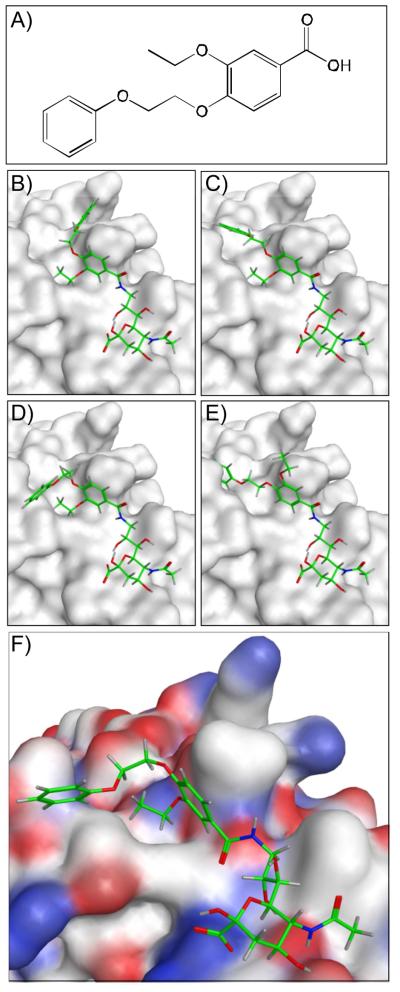
Figure 1.
Representative structures from the in silico screening strategy to identify high affinity ligands of Sialoadhesin (Sn). (A) Representative carboxylic acid from a commercial building block library that were screened as potential substituents of 9-NH2-Neu5Ac. (B-E) Four representative solutions from the tethered docking approach highlighting varying docking poses of the tethered acid substituent. Conformations of the respective substituents were calculated and conjugated via in silico amide coupling to 9-NH2-Neu5Ac, which was fixed within the binding site. The top 3000 hits from this initial docking evaluation were further inspected using AutoDock. (F) Representative AutoDock solution for the selected carboxylic acid coupled to 9-NH2-Neu5Ac. Oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen atoms are highlighted in red, white, and blue, respectively.