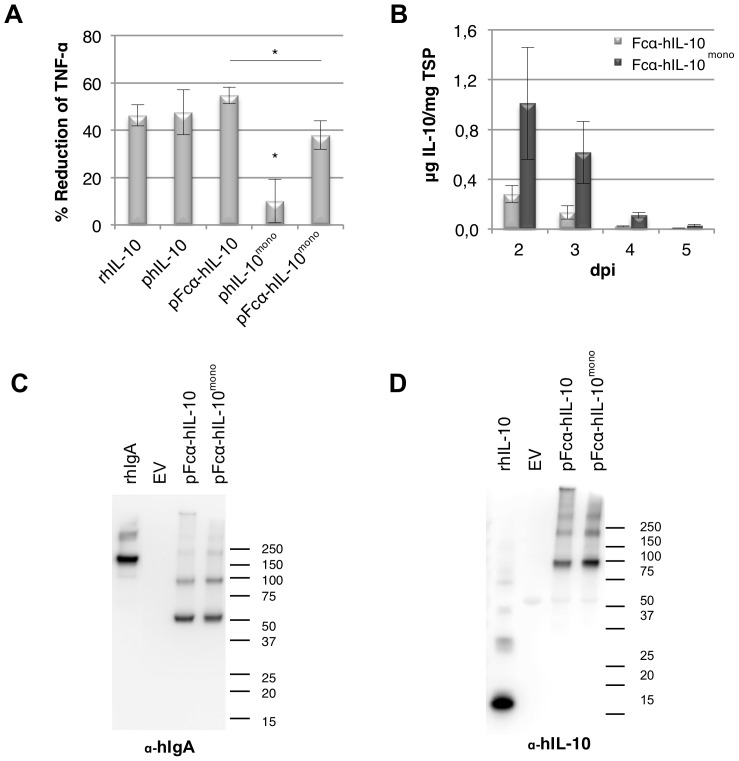
Figure 6. Analysis of biological activity and expression of human IL-10 and human IL-10mono fused to Fcα.
Forced dimerization of human IL-10mono restores biological activity. (A) Bioactivity assay of hIL-10mono and Fcα-hIL-10 fusion proteins on mouse macrophages (RAW267.4). Plant produced (p) and recombinant (r) E. coli produced hIL-10 were calibrated to contain the same amount of IL-10 as well as total soluble protein by using the empty vector control. Cells were then pretreated with 50 ng/ml hIL-10 for 20 min and subsequently stimulated with 1 µg/ml E. coli lipopolysaccharide. Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) expression was determined by ELISA and IL-10 activity is indicated as the percentage of inhibition of TNF-α expression as compared to the empty vector control (n = 4, error bars indicate standard error). Significant difference (P<0.05) between samples is indicated with an asterisk, where biological activity of hIL-10mono was significantly different to all other samples. (B) Yield of human (h) IL-10 in crude extracts 2 to 5 days post infiltration as determined by ELISA (n = 3, error bars indicate standard error). (C/D) Western blot analysis under non-reducing conditions of plant produced (p) Fcα-hIL10 and Fcα-hIL-10mono using an antibody raised against human IL-10 and human IgA for visualization, respectively. As controls, empty vector (EV), 50 ng recombinant (r) E. coli produced hIL-10 and 10 ng purified hIgA were used. A molecular weight marker is indicated in kDa.