Fig. 4. TDG glycosylase recognizes and excises 5caC from DNA.
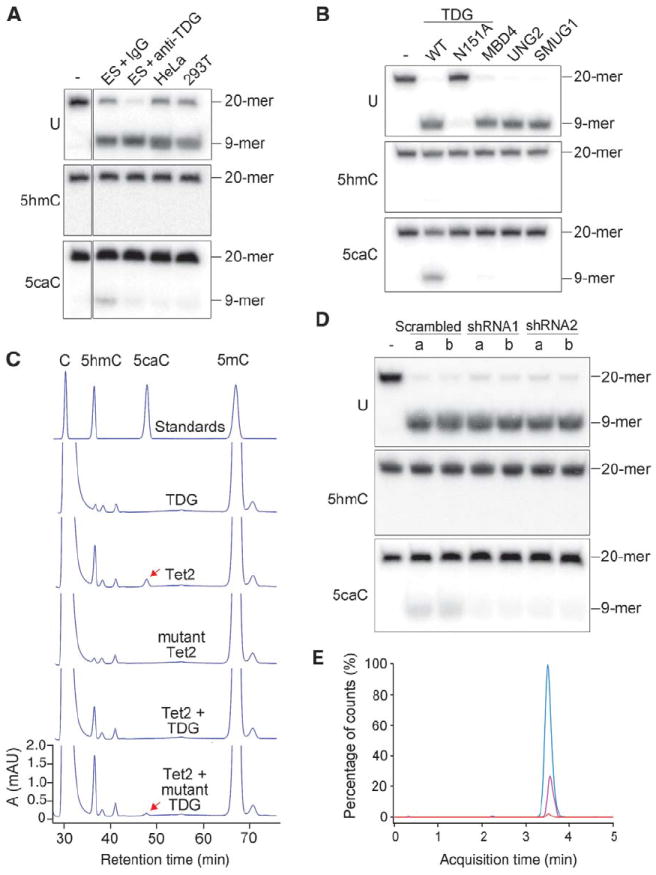
(A) ES cell nuclear extract contains 5caC-specific base-excision activity. The activity in the nuclear extract of mouse ES cells to generate alkaline-sensitive sites was assayed by using 5caC-containing oligonucleotide duplexes. Shown are the results obtained with 20-mer DNA duplexes containing either G/U (U), G/5hmC (5hmC), or G/5caC (5caC) base pairs in the middle. (B) Excision of 5caC from DNA by Flag-TDG but not by Flag-MBD4, Flag-UNG, or GST-SMUG1. Asn151→Ala151 (N151A) is a catalytically inactive mutant of TDG. Proteins used are shown in fig. S10B. 6xHis-TDG purified from bacteria was also active in 5caC excision. TDG displayed a much stronger glycosylase activity for the “hemi-carboxylated” DNA substrate containing 5caC only on one strand (fig. S11). WT, wild type. (C) Reduced 5caC formation by cotransfection of TDG in HEK 293T cells expressing ectopic Tet2. The mutant TDG was as in (B). (D) Lack of 5caC base-excision activity in Tdg knockdown ES cells. Nuclear extracts prepared from the two independent cell lines (a and b) containing shRNA knockdown construct 1, 2, or scramble control were tested as in (A). (E) HPLC-MS/MS detection of 5caC in ES cells depleted of TDG. MRM profiles of hydrolysates of genomic DNA from control (red) and TDG-depleted ES cells (pink) were analyzed. Synthetic 5caC nucleoside was used as a positive control (blue). Depletion of TDG was confirmed by Western analysis of independent stable knockdown ES cell lines (fig. S12).
