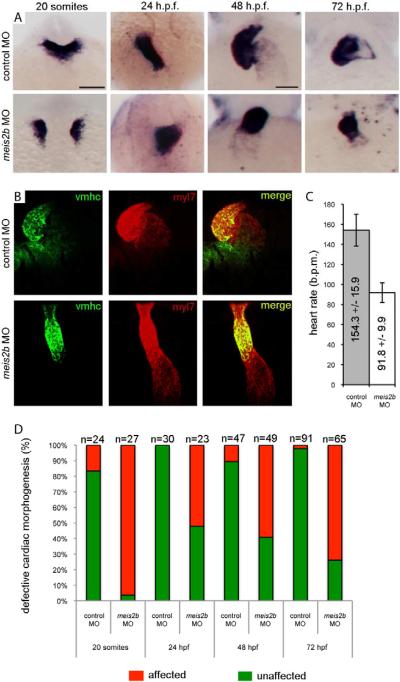
Figure 5. meis2b is required for cardiac morphogenesis.
(A) Expression of myl7 at 19 h.p.f., 24 h.p.f, 48 h.p.f. and 72 h.p.f. in control-MO (top row) versus meis2b-MO (bottom row) injected zebrafish embryos. Dorsal view, anterior is up in 20 somite and 24 h.p.f. embryos. Ventral view, anterior up in 48 h.p.f. and 72 h.p.f. embryos. At 19 h.p.f., meis2b-MO injected embryos display defects in fusion of the myl7+ cardiac progenitors at the midline compared with control-MO injected embryos. By 24 h.p.f., the heart tube has formed in meis2b morphants but displays aberrant cardiac morphogenesis and is either sitting at the midline or moving down the right side of the embryo, compared with the control-MO injected embryos where normal heart development proceeds with the heart tube emerging from under the head, down the left side of the embryo. At 48 and 72 h.p.f., control MO injected embryos display normal cardiac looping, while meis2b-MO injected embryos' hearts have not looped. (B) This failure of cardiac looping in meis2b-MO injected embryos is further evident in vmhc (green) and myl7 (red) double fluorescent in situs at 48 h.p.f.. (C) Heart rate is significantly reduced in meis2b-MO injected embryos compared with control-MO injected embryos at 72 h.p.f. (b.p.m. = beats per minute) Mean heart rate +/− s.d. is shown, n=10. P = 4 ×10−9 (Student's t-test, two-tailed). (D) Percentages of embryos displaying the depicted phenotypes. Scale bar in A (top left), 100 μm. Scale bar in A (top 3rd from the left), 50 μm. See also Figure S5.