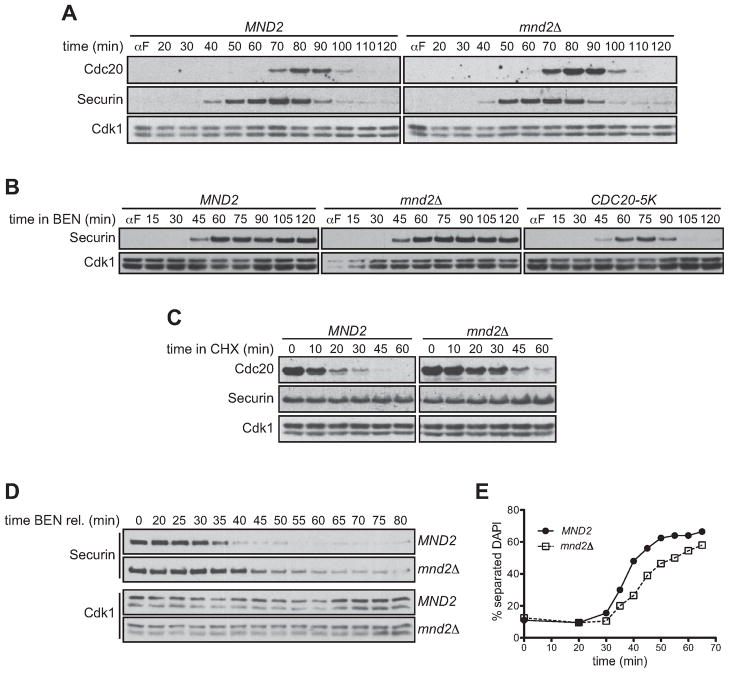
Figure 6. Mnd2 is required for efficient checkpoint release.
(A) Asynchronous log-phase cultures of MND2 or mnd2Δ cells were arrested in G1 with α-factor. α-factor was washed out and cells were harvested at the indicated times. αfactor was re-added when a majority of the cells had budded. Samples were analyzed by western blotting. Similar results were obtained by flow cytometry analysis of DNA content (data not shown).
(B) Asynchronous log-phase cultures of MND2, mnd2Δ, or CDC20-5K cells were arrested with α-factor and released into media containing 60 μg/ml benomyl. Cells were harvested at the indicated times and α-factor was re-added when a majority of the cells had budded. Samples were analyzed by western blotting.
(C) MND2 or mnd2Δ strains were arrested in benomyl before addition of cycloheximide. Samples were analyzed by western blotting.
(D) Asynchronous log-phase cultures of MND2 or mnd2Δ cells were arrested with αfactor and released into media containing 60 μg/ml benomyl. Cells were released from benomyl into α-factor and harvested at the indicated times. Samples were analyzed by western blotting.
(E) Cells from an experiment like that in panel (D) were analyzed for separation of DNA masses by DAPI staining. Two hundred cells were counted per time point. A similar delay was obtained by counting the percent of large budded cells and by flow cytometry analysis of DNA content (data not shown).