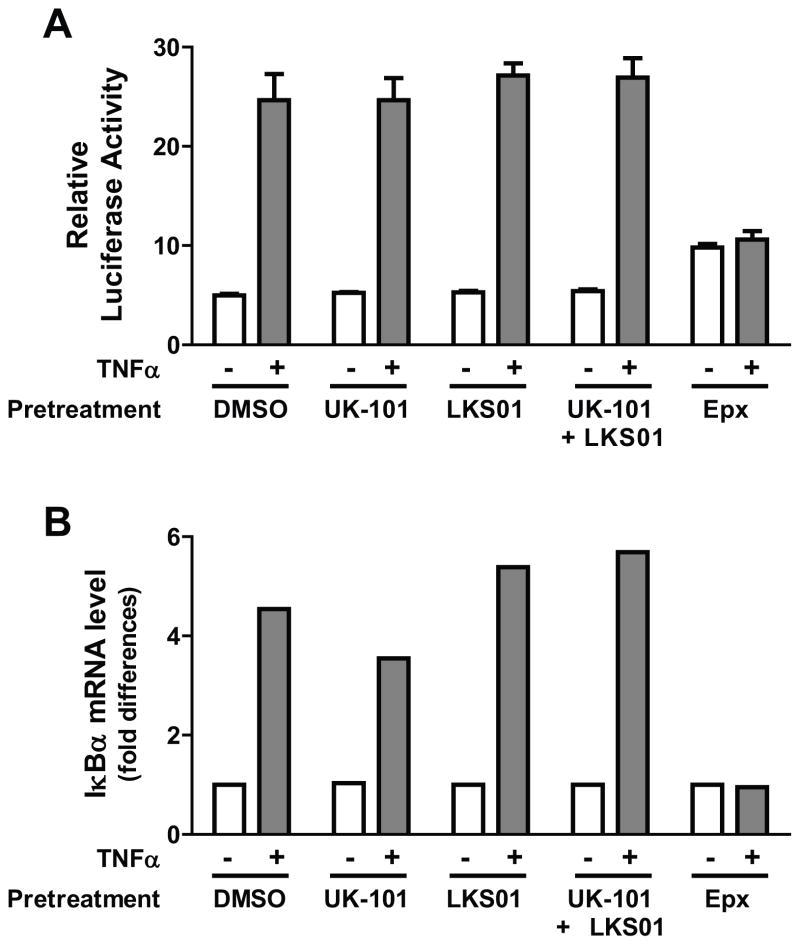
Fig. 5.
Selective inhibition of β1i, β5i or both using UK-101 or LKS01 does not block NF-κB-mediated transcriptional activation induced by TNFα. (A) Results using an NF-κB reporter plasmid show that the stimulatory effect of TNFα on NF-κB transcriptional activity is maintained in H23 cells pretreated with UK-101 (1 μM) or LKS01 (0.2 μM), either individually or in combination. In contrast, pretreatment with epoxomicin (1 μM) led to a slightly increased reporter gene expression and no further TNFα-stimulated NF-κB transcriptional activity. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR results show that the stimulatory effect of TNFα on the IκBα transcript, a downstream target of NF-κB, is maintained in H23 cells pretreated with UK-101 (1 μM) or LKS01 (0.2 μM), either individually or in combination. In contrast, pretreatment with epoxomicin (1 μM) led to no changes in IκBα transcript levels by TNFα.