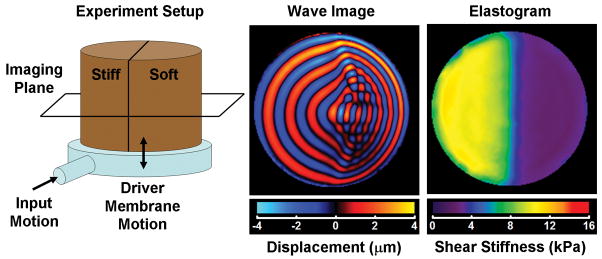
Figure 1.
The diagram on the left depicts an MRE experiment performed on a 2-layer bovine gelatin phantom made of a stiff gel and a soft gel. The phantom rests on a plastic drum driver supplied with time-harmonic pressure variations that flex the membrane of the driver. As the phantom shakes up and down, shear waves are produced at the edge of the phantom (due to inertial effects) that propagate into the phantom. The phantom was imaged in the coronal imaging plane. The middle image shows a wave image from an MRE acquisition performed with motion encoding in the through-plane direction. The difference in the shear wavelength in the two regions is evident with the wavelength being longer in the stiff region. The image on the right is an elastogram of the phantom indicating the stiff and soft regions.