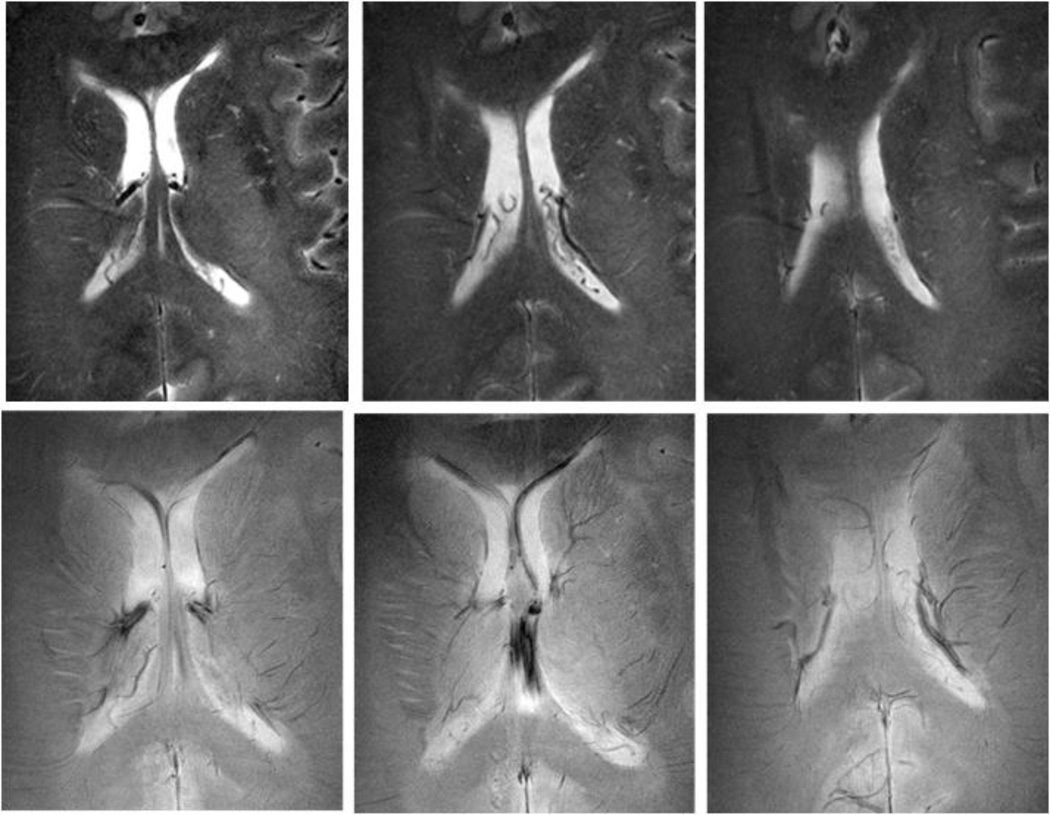
Figure 2.
High resolution anatomical images obtained using 8Tesla MRI, a 45-year-old woman with a small vessel disease. Rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement (RARE) images (A, B, C) at the level of ventricles showed confluent white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) extending from the anterior and posterior horns of the ventricles (white arrows). Additional focal areas of high signal intensity were seen in the periventricular white matter and basal ganglia. 8T GE images (D, E, F) showed normal pattern of microvasculature as signal voids (black arrows).(GE: BW=69.4 kHz, FOV=20×20cm, slice thickness 2.3 mm, TR=600 ms, TE=10 ms, matrix 1024 × 1024; RARE: BW=69.4 kHz, FOV=20 × 20 cm2, slice thickness 2 mm, TR=3000 ms, TE=22 ms, matrix 512 × 512, RARE factor 4). (Reproduced with permission from: Novak V, Christiforidis G: Clinical promise. In: Robitaille PM, Berliner LJ, editors. Ultra high field magnetic resonance imaging (UHFMRI): Theory and applications, biological magnetic resonance. A series of contemporary topics and reviews. (With permission from: Novak V. Clinical Promise: Clinical Imaging at Ultra High Field. 2007; 26(13): 411–437) [77].