Fig. 2.
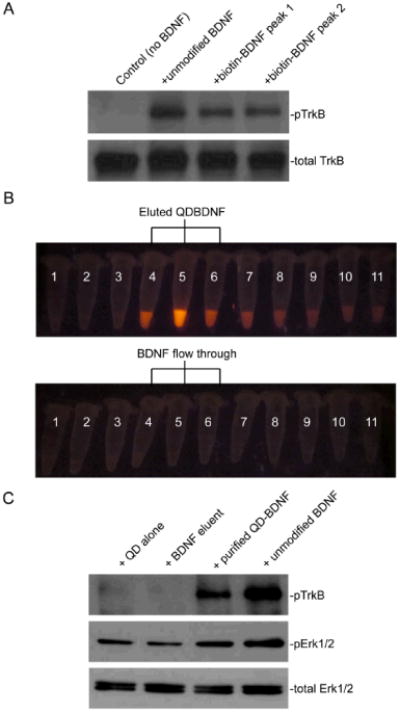
Biotin-BDNF and QD-BDNF are biologically active. (A) Western blot against phospho-TrkB showed that BDNF and biotin-BDNF collected from both HPLC peaks induced TrkB phosphorylation in a TrkB-expressing 3T3 cell line. (B) Separation of QD-BDNF from free BDNF by a size-exclusion column. QD-BDNF was loaded into a Sephacryl column and elution fractions were collected into separate tubes (50 μl each). Tubes with the most intense QD fluorescence (Tube 4, 5 and 6 in the top row) were pooled together as purified QD-BDNF. Unmodified BDNF was loaded into the same column and eluted under the same conditions. Elution fractions 4, 5 and 6 (bottom row), labeled as BDNF eluent, were used as a negative control. (C) Purified QD-BDNF induced TrkB phosphorylation in TrkB-3T3 cells and Erk phosphorylation in hippocampal neurons. pTrkB was immunoprecipitated with the pTrk antibody before western blot. No activity was detected by the BDNF eluent, indicating that free BDNF was not eluted out in the same fractions as QD-BDNF.
