Fig. 4.
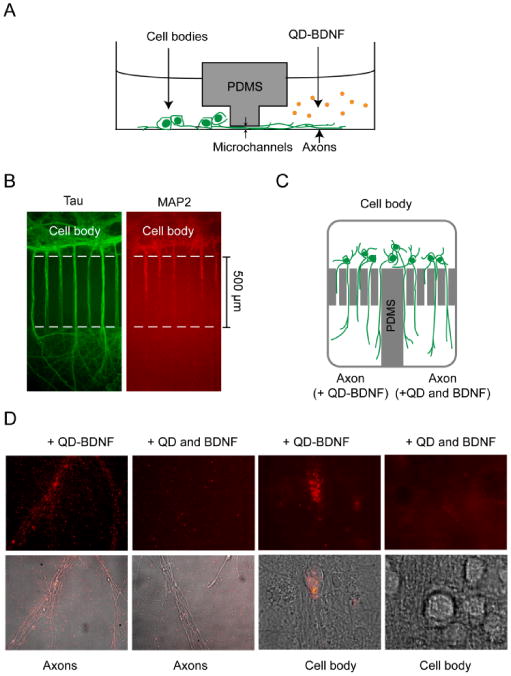
Compartmentalized culture of hippocampal neurons and transport of QD-BDNF in microfluidic devices. (A) Schematic drawing of a microfluidic device for compartmentalized neuronal culture (side view). The cell body and axon compartments are connected only through a set of microchannels. (B) Immunostaining showed that only axons (stained with anti-Tau, green) grew across the microchannels into the axon compartment while dendrites did not (stained with anti-MAP2, red). (C) Design of a microfluidic device that has a single cell body compartment but two axon compartments (top view). This device was used to compare transport of QD-BDNF against QD mixed with unmodified BDNF. QD-BDNF was added to one axon compartment while a mixture of QD and unmodified BDNF was applied to the other axon compartments. (D) After overnight incubation at 37 °C, QD-BDNF (1 nM) staining of axons was extensive in the axon compartment. On the other hand, very few QDs overlapped with axons on the side where a mixture of 1 nM QD and 1 nM unmodified BDNF was applied. QD fluorescent signal in cell bodies was only found on the side applied with QD-BDNF.
