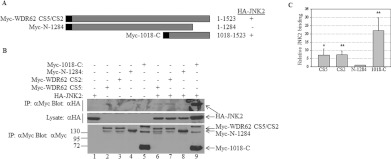
Figure 2. WDR62 C-terminal domain is necessary for JNK association.
(A) Schematic representation of the WDR62 deletion constructs used in the experiments. Amino acid positions are numbered. The black square represents the position of the Myc epitope tag. Summary of the binding of the various WDR62 truncations to HA–JNK2 is indicated by + and −. (B) HEK-293T cells were transfected with full-length Myc-WDR62 CS2 and CS5 isoforms, the WDR62 C-terminus fragment (Myc-1018-C) or the C-terminal truncation mutant alone (Myc-N-1284), or with HA–JNK2 as indicated. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-Myc antibodies followed by Western blotting with either anti-HA or anti-Myc antibodies (top panel and bottom panel respectively). The expression level of HA–JNK2 was determined by blotting the total cell lysate with anti-HA antibody (middle panel). The migration of the relevant proteins is indicated by arrows. Molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left-hand side of the bottom panel. (C) Quantification of JNK2 binding as described in (B). JNK2 association with Myc-N-1284 is considered as 1 and the extent of JNK2 binding of the other WDR62 truncations is calculated relatively. Results shown are means±S.D. for three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.