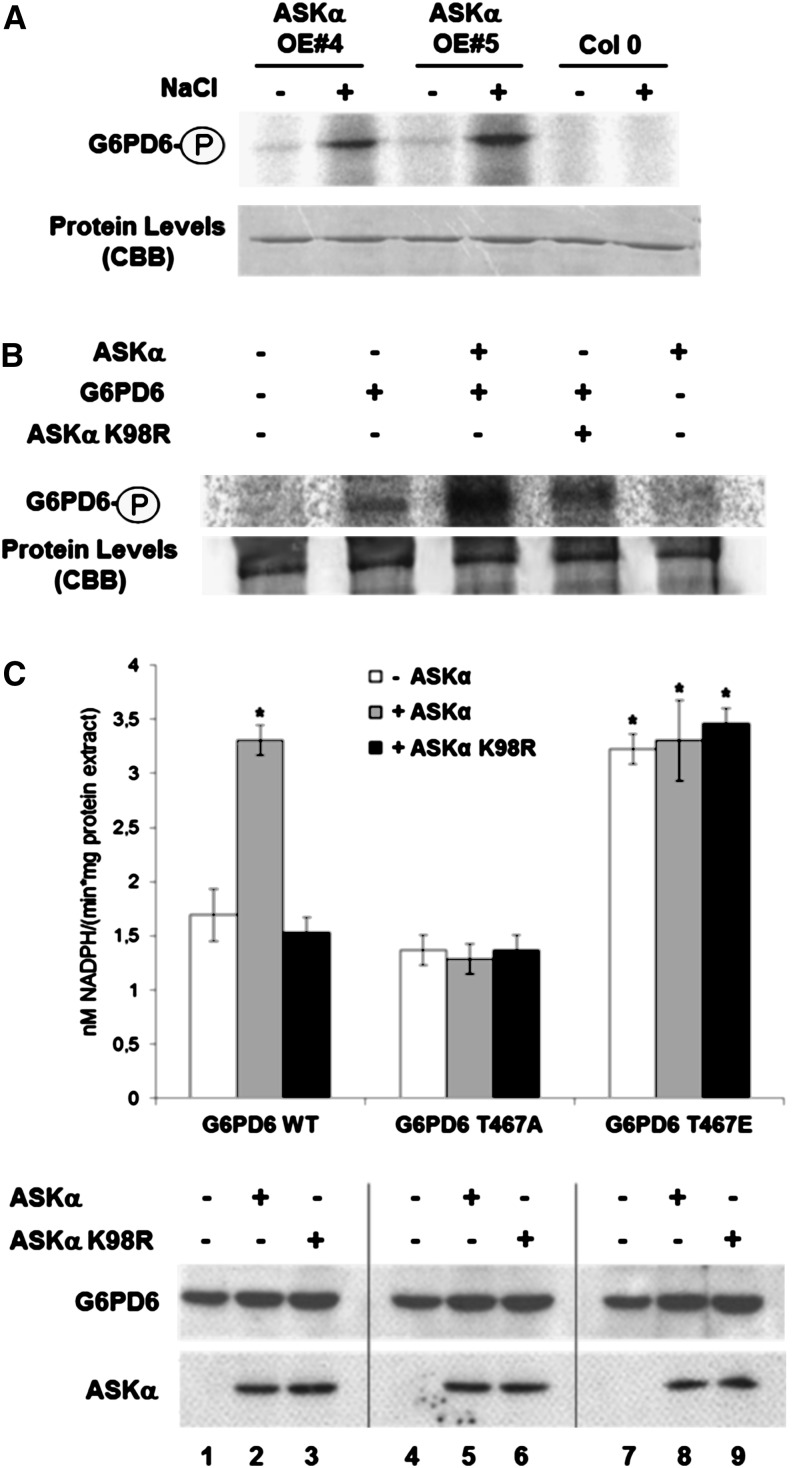
Figure 5.
ASKα Activates G6PD6 in Vivo.
(A) Phosphorylation of G6PD6 by immunoprecipitated ASKα. Immunokinase assay using anti-myc antibodies (Santa Cruz) to purify ASKα-myc from nonstressed and high salinity–stressed ASKα-myc–expressing plants (same plant material as in Figure 1D) using GST-G6PD6 as a substrate.
(B) G6PD6 is an in vivo phosphoprotein. Arabidopsis protoplasts were transformed with G6PD6-HA or cotransformed with G6PD6-HA and ASKα-myc or ASKα K98R-myc and labeled with 32P-orthophosphate. The autoradiogram shows G6PD6 immunoprecipitated from 200 µg of protein extracts with HA antibodies. ASKα K98R-myc and untransformed protoplasts were used as specificity controls for phosphorylation and immunoprecipitation.
(C) In vivo activity of G6PD6, G6PD6 T467A, and G6PD6 T467E. G6PD activity (top) and protein levels (bottom) of Arabidopsis protoplasts transformed solely with G6PD6-HA, G6PD6-HA T467A, and G6PD6-HA T467E (lanes 1, 4, and 7, respectively), or cotransformed either with ASKα-myc (lanes 2, 5, and 8) or with ASKα K98R-myc (lanes 3, 6 and 9). Data are means ± sd. The assay was repeated three times. Asterisks indicate a significant difference (*P < 0.05) using Student’s t test for pairwise comparison to cells solely transformed with wild-type G6PD6-HA. WT, the wild type.