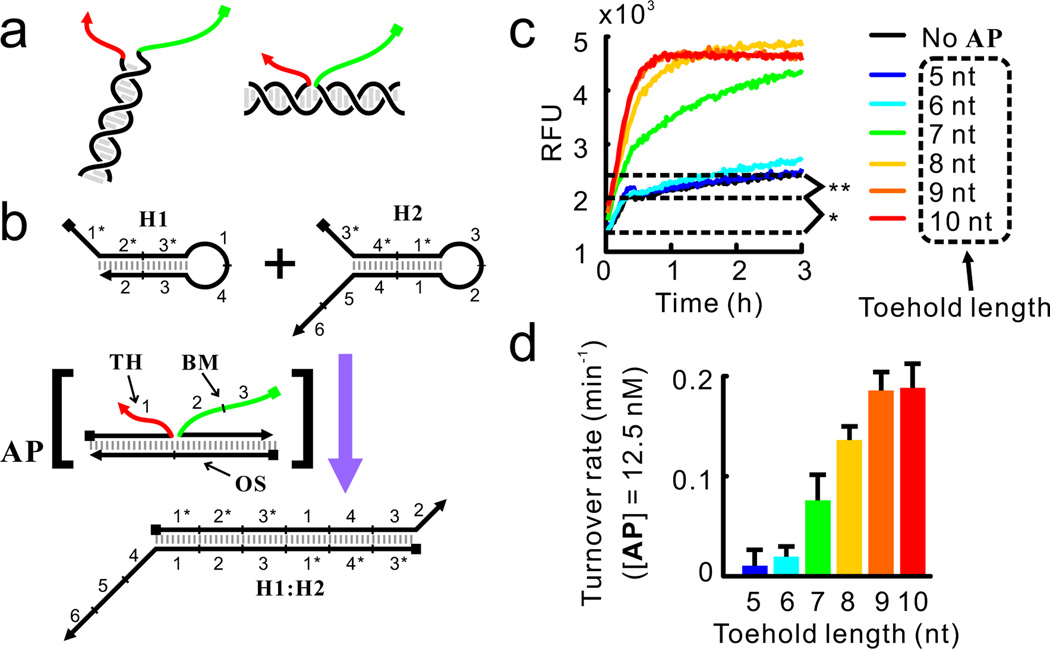
Figure 2.
Feasibility of detecting HCR product using CHA-based circuits. (a) Toehold (red) and branch-migration domain (green) co-localized by direct (left) or indirect (right) hybridization. (b) Structure of the substrates (H1 and H2) and the catalyst (AP complex) of the CHA reaction. The toehold and branch-migration domain in the AP complex are shown in red and green, respectively. Detailed reaction pathway is shown in Figure S2. The fluorescent reporter for H1:H2, named Reporter, is similar to the Reporter2 complex shown in Figure 1c and is not shown here. (c) Kinetics of the CHA reaction catalyzed by the AP complex with different toehold length. In all reactions, [H1] = 75 nM, [H2] = [Reporter] = 50 nM, [TH] = [BM] = 15 nM, [OS] = 12.5 nM. Symbols * and ** denote two types of circuit leakage which are further discussed in Figure S1. (d) Turnover rates (rates of reaction divided by concentration of the catalyst) as function of toehold lengths.