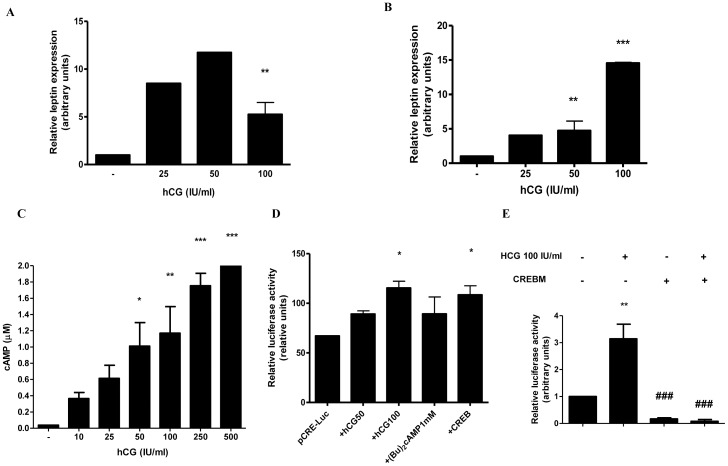
Figure 1. hCG stimulates leptin mRNA expression and enhances cAMP levels in placenta.
(A) JEG-3 cells (1×106 cells) were plated in complete DMEM-F12 media supplemented with 1% FBS and incubated during 3 days with different doses of hCG (IU/ml). (B) Placental explants were obtained as indicated in Materials and Methods and treated with increasing hCG concentrations. In (A) and (B), total RNA was extracted as described in Material and Methods. Leptin mRNA was quantified by real time RT-PCR. Cyclophilin was used as internal standard. (C) BeWo cells (1×105) were seeded in 96-well plate and treated during 24 h with increasing concentrations of hCG, as indicated. cAMP-Glo assay kit was used to measure intracellular cAMP concentration. (D) Cells were transiently transfected with pCre-Luc plasmid construction and treated with hCG, (Bu)2cAMP or cotransfected with CREB, as indicated, during 72 h in DMEM-F12 media supplemented with 1% FBS. Luciferase activity was measured in cellular extracts and normalized to β-galactosidase activity. Activity obtained with empty vector (PGL-3 basic vector) was set as a control. (E) BeWo cells were transiently transfected with pL1951 and treated with 100 IU/ml hCG and/or cotransfected with CREBM plasmid. Cells were incubated during 72 h in DMEM-F12 1% FBS media. Luciferase activity was measured in cellular extracts and normalized to β-galactosidase activity. Activity obtained with empty vector (PGL-3 basic vector) was set as a control. Results shown are from a representative experiment and are expressed as means ± S.E.M. for three independent experiments performed in duplicates. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs control; ###p<0.001 vs hCG treatment.