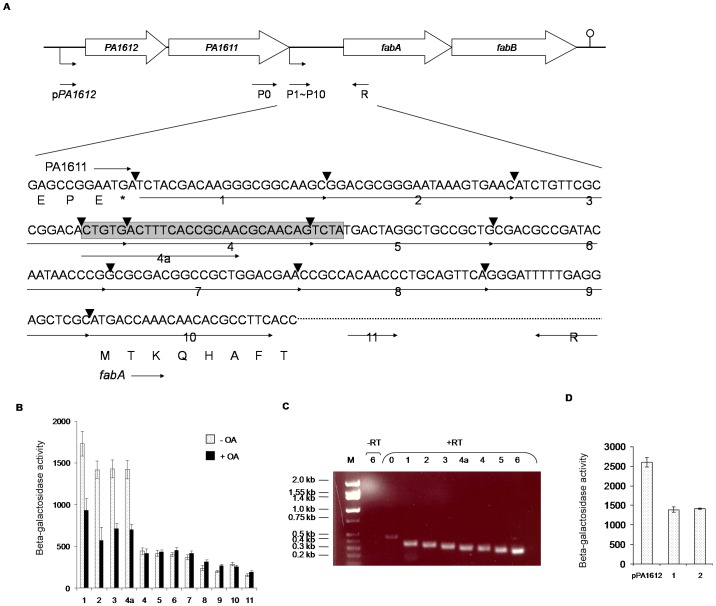
Figure 3. Characterization of fabA regulatory region.
A) Positions of primer-binding sites in the fabA-PA1611 intergenic region. Each primer is symbolized as follows: P0, fabA0; P1-P11, fabA1-attB2 through fabA11-attB2; R, fabA-attB1. Primer P11 is placed at the 124th–144th nucleotide from the first nucleotide of the fabA coding region. The sequence shaded and boxed in the gray box indicates the putative 30 bp regulatory element. Vertical arrow heads indicate the end points of sequences present in the lacZ fusion constructs analyzed in Fig. 3B. B) The 30 bp sequence is important for fabAB expression. PAO1 contained fabA′-lacZ vectors with fabA upstream regions amplified with primers 1 through 11. The 5 bp addition in primer 4a, which restores a complete 30 bp sequence, recovered lacZ expression indicating that it is important for fabA transcription. Cells were grown and β-galactosidase activities were measured as described in the legend to Fig. 2 with and without oleate (OA) supplementation. C) Characterization of the promoter region of fabA using RT-PCR analysis of fabA expression. RNA was extracted from PAO1 grown at 37°C using the hot phenol extraction method. cDNA was synthesized using the Superscript III First-strand kit (Invitrogen) and primer R. Resulting cDNAs were used as templates for PCR amplification utilizing primer R and the indicated primers (see Fig. 3A for location of primer-binding sites). D) β-galactosidase activities in PAO1 containing lacZ fusions with various fabA upstream fragments. The upstream fragments were amplified with primers pPA1612, and primers p1 and p2 (see Fig. 3A for primer-binding sites).