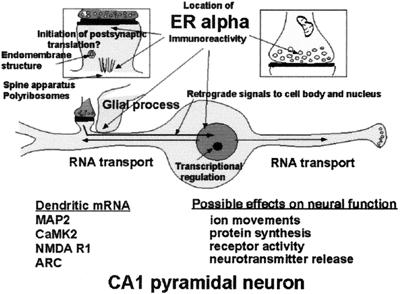
Figure 8.
Schematic depiction of ER localization in CA1 pyramidal neurons that respond to E with synapse formation. ERα is found in dendrites, presynaptic terminals, glia, and the nuclear envelope of some principal cells, as well as in cell nuclei of inhibitory interneurons (not shown). Glia may be involved in synapse formation and/or removal. Dendrites are sites of protein synthesis on polyribosomes and at endomembrane structures using RNAs transported from the cell body (see text). Non-nuclear ER may be involved in other E effects linked to second messenger activation on processes such as neurotransmitter release and phosphorylaton of neurotransmitter receptors and ion channels. Second messenger activation by E in nerve terminals, dendrites, and glial cell processes may result in retrograde second messenger signals, such as phosho-CREB and P-Akt, that return to signal the genome.