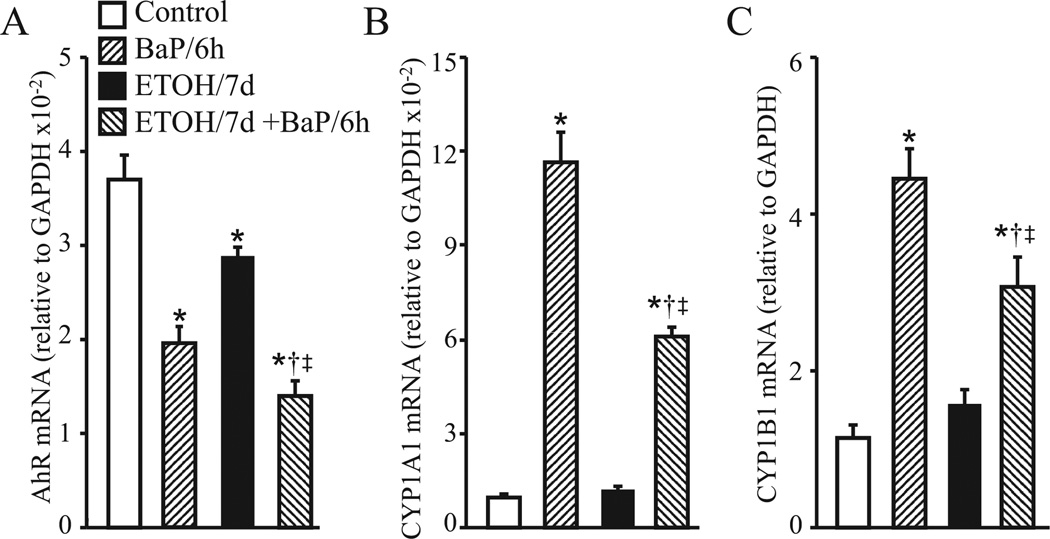
Fig. 6.
The effect of chronic ethanol (EtOH) exposure on benzo (a)pyrene (BaP)-induced changes in expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A1, and 1B1. Mouse hepatic stellate cells were incubated with culture medium alone (control), 10 nM BaP for 6 hours (BaP/6 h), 50 mM EtOH for 7 days (EtOH/7 d), or 50 mM EtOH for 7 days followed by 10 nM BaP treatment for another 6 hours (EtOH/7 d + BaP/6 h). For cells that were not treated with BaP, an equal amount of vehicle dimethyl sulfoxide was added to the culture medium. The levels of AhR, CYP1A1, and CYP1B1 mRNAs were determined by quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA. Values represent the mean ± SEM of 5 independent experiments. *p < 0.05 versus cells without EtOH treatment (control), †p < 0.05 versus cells treated with 50 mM EtOH alone for 7 days, ‡p < 0.05 versus cells treated with BaP but without EtOH.