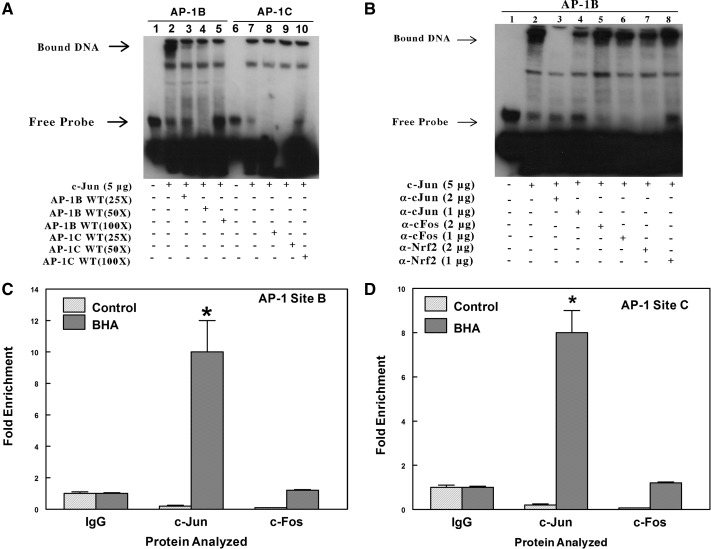
Fig. 7.
EMSA analysis indicates the formation of a nuclear protein complex with the AP-1-like element at site B (position −758) but not with the AP-1-like element at site C (position −1069). A, biotin-labeled double-stranded probes were incubated for 20 min with 5 μg of nuclear extracts from HepG2 transfected with c-Jun expression plasmids. In the competition experiments, a 25- to 100-fold excess of unlabeled double-stranded probes was included in the binding reactions. The protein-DNA complexes were resolved by electrophoresis and detected using chemiluminescence. The result shown in this figure was identical to that of three other independent experiments. B, analysis using precipitating antibodies confirms that a protein in the nuclear extract that binds to the AP-1 site B is c-Jun and not c-Fos or Nrf2. EMSAs were performed by incubating nuclear extracts from HepG2 cells overexpressing c-Jun with a biotin-labeled probe containing the AP-1B site of the mouse Aldh1a1 promoter. In SuperShift experiments with antibodies, the binding reactions were incubated with either 1 or 2 μg of rabbit polyclonal c-Jun or c-Fos or Nrf2 antibodies for 30 min at 4°C. The figure is a representative of three other independent experiments. C, ChIP analysis to examine in vivo binding of c-Jun and c-Fos to the AP-1 at site B. Chromatin was prepared from the liver of control or BHA-treated C57BL/6J mice. The complexes containing cross-linked DNA binding proteins to their cognate cis-element were pulled down with antibodies against IgG, c-Jun, or c-Fos conjugated to Dynabeads protein A/G. The purified DNA was analyzed by real-time PCR with primers spanning AP-1 sites B or C in the proximal promoter of the Aldh1a1 gene. *, p < 0.05, significantly different compared with nonimmune immunoglobulin (Student's t tests). D, ChIP analysis to examine in vivo binding of c-Jun and c-Fos to the AP-1 at site C. *, p < 0.05, significantly different compared with nonimmune immunoglobulin (Student's t test).