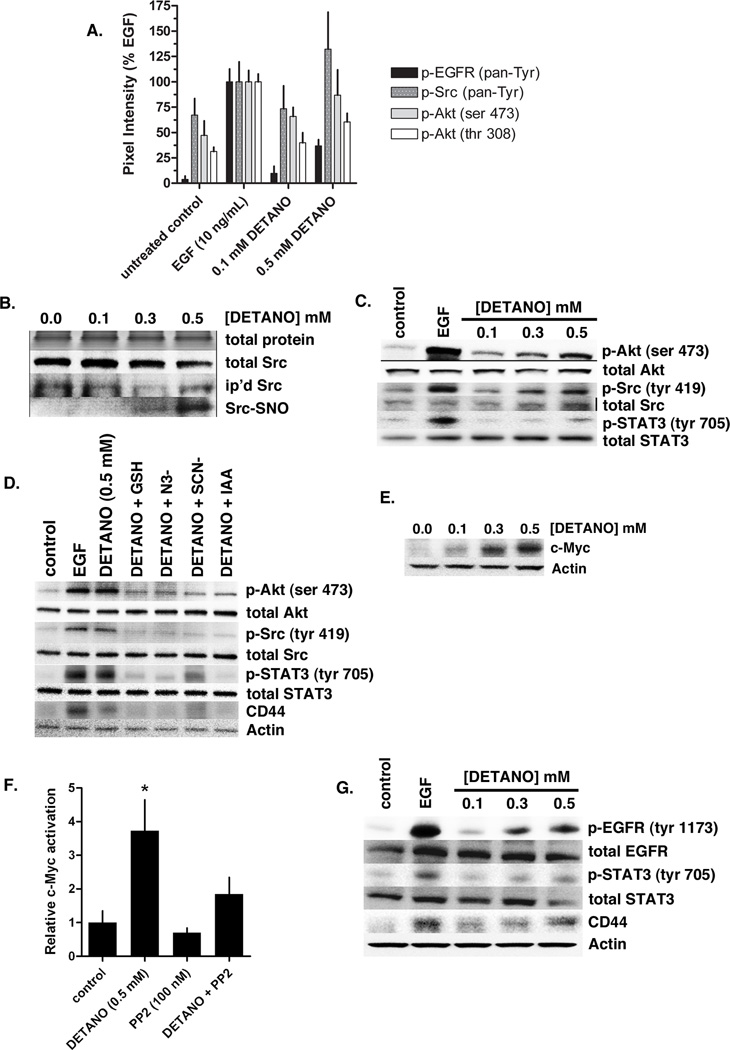
Figure 3. NO activates EGFR and Src kinase signaling pathways in ER− breast cancer cells.
(A) Densitometric analyses from receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) Pathscan spot-ELISA experiment in MDA-MB-468 cells treated with EGF or DETANO compared to serum-starved controls. EGFR, Src and Akt phosphorylation was increased by EGF and 0.5 mM DETANO. (B) Total input protein and Src, immunoprecipitated and S-nitrosated (SNO) Src from MDA-MB-468 cells treated with DETANO. (C) Relative Akt, Src and STAT3 phosphorylation from MDA-MB-468 cells treated with either EGF or DETANO compared to untreated serum-starved controls. (D) Akt, Src, STAT3 phosphorylation and CD44 expression in the presence of chemical inhibitors of nitrosation. (E) Western blot showing the stabilization of c-Myc in MDA-MB-468 cells in response to DETANO concentration. (F) Relative c-Myc-DNA binding from MDA-MB-468 cells treated with 0.5 mM DETANO and/or PP2 (100 nM). Normalized mean c-Myc activity (± sd) is shown. Statistical significance was determined by *P < 0.05. (G) Representative western blots from Her2+ SKBR3 cells exposed to EGF or DETANO showing NO-induced increases in EGFR and STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation and increased CD44 expression.