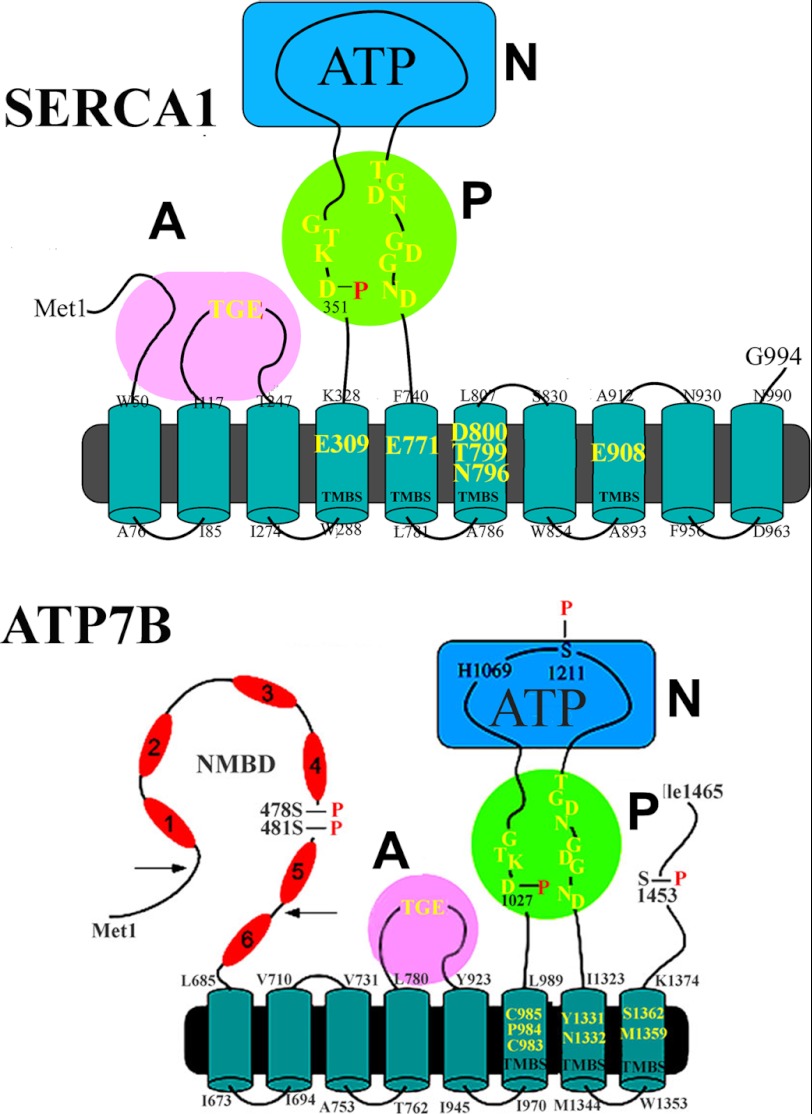
FIGURE 1.
Two-dimensional folding models of the SERCA (upper panel) and ATP7B (lower panel) sequences. The diagrams show 10 (SERCA) or 8 (ATP7B) transmembrane segments including the calcium or copper binding sites (TMBS) involved in enzyme activation and transport. The extramembranous region of both enzymes comprises a nucleotide binding domain (N), the P domain, with several residues (in yellow) conserved in P-type ATPases, including the aspartate (Asp-351 or Asp-1027) that undergoes phosphorylation to form the catalytic phosphoenzyme intermediate (EP), and the A domain with the TGE conserved sequence involved in catalytic assistance of EP hydrolytic cleavage. The His-1069 residue whose mutation is frequently found in Wilson disease is shown on the N domain of ATP7B. Specific features of ATP7B are the N-metal binding domain (NMBD) extension with six putative copper binding sites and serine residues undergoing kinase-assisted phosphorylation (Ser-478, Ser-481, Ser-1211, Ser-1453).