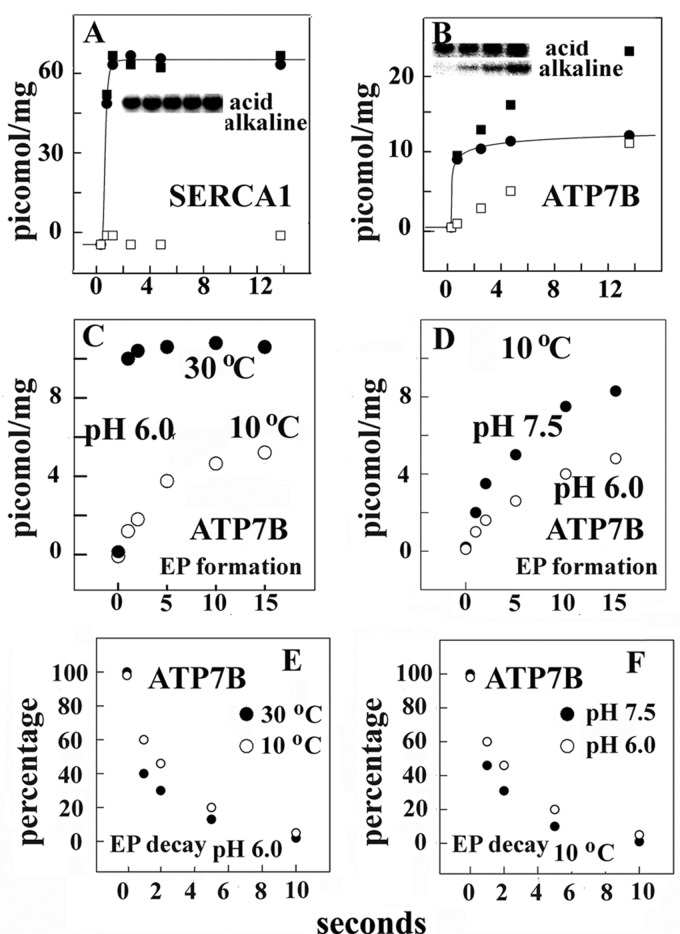
FIGURE 4.
Phosphoprotein formation after the addition of ATP to recombinant SERCA (A) or ATP7B (B–D) and subsequent decay of ATP7B phosphoenzyme (E and F). Microsomes obtained from COS-1 cells sustaining heterologous expression were incubated with 50 μm [γ-32P]ATP at 10 or 30 °C at various pH levels as explained under “Experimental Procedures.” Electrophoresis in acid buffer or alkaline buffer was then performed to distinguish total [32P]phosphoprotein (■) from alkali-resistant [32P]phosphoprotein (serine and/or threonine, □). The difference is considered alkali-labile [32P]phosphoprotein (aspartate, ●) and attributed to formation of phosphorylated enzyme intermediate. acid and alkaline refer to the media used for resuspension of samples and electrophoresis. Electrophoretic gel images correspond to sequential samples obtained within the time scale shown in the horizontal axis. Note that no alkaline-resistant phosphoprotein was obtained with SERCA, whereas both alkaline-resistant and alkaline-labile phosphorylation were obtained with ATP7B. Only the difference (phosphorylated enzyme intermediate) is shown in the lower panels (C–F). Decay of phosphoenzyme was measured as explained under “Experimental Procedures” and in the legend to Fig. 3. The experimental points are averages of values obtained in three to four different experiments. The electrophoretic images in A and B are examples of data repeated in all experiments.