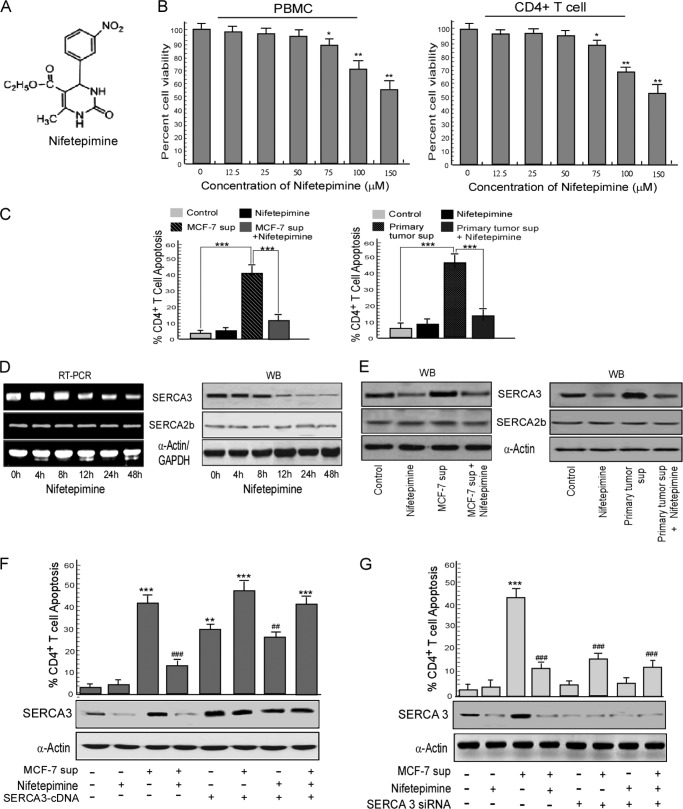
FIGURE 2.
Nifetepimine-induced SERCA3 down-modulation protects CD4+ T cells from tumor-induced apoptosis. A, shown is the structure of nifetepimine. B, human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) as well as CD4+ T cells were treated with different doses of nifetepimine for 24 h and scored for percent apoptosis by annexin-V/7-AAD positivity. C, shown is a graphic representation of CD4+ T cell apoptosis in control and MCF-7/primary tumor supernatant (sup)-treated CD4+ T cells in the presence and absence of nifetepimine. D, CD4+ T cells treated with nifetepimine for different time periods were examined for SERCA3 and SERCA2b expression at both mRNA and protein levels and by RT-PCR and Western blotting (WB), respectively. E, shown is a Western blot representation for SERCA3 and SERCA2b in control and MCF-7/primary tumor supernatant-treated CD4+ T cells in the presence and absence of nifetepimine. F, shown is a graphic representation of CD4+ T cell apoptosis in control and tumor supernatant-treated SERCA3 overexpressed CD4+ T cells in the presence and absence of nifetepimine. * denotes p value with respect to the control, and # denotes p value with respect to the tumor supernatant. Under similar experimental conditions, SERCA3 levels were determined by Western blot analysis. G, a graphic representation shows annexin V positivity for CD4+ T cell from control and tumor supernatant-treated SERCA3 knocked-down sets in the presence and absence of nifetepimine. * denotes p value with respect to the control, and # denotes p value with respect to the tumor supernatant. GAPDH and α-actin were used as internal control. Values are the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments in each case. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001.