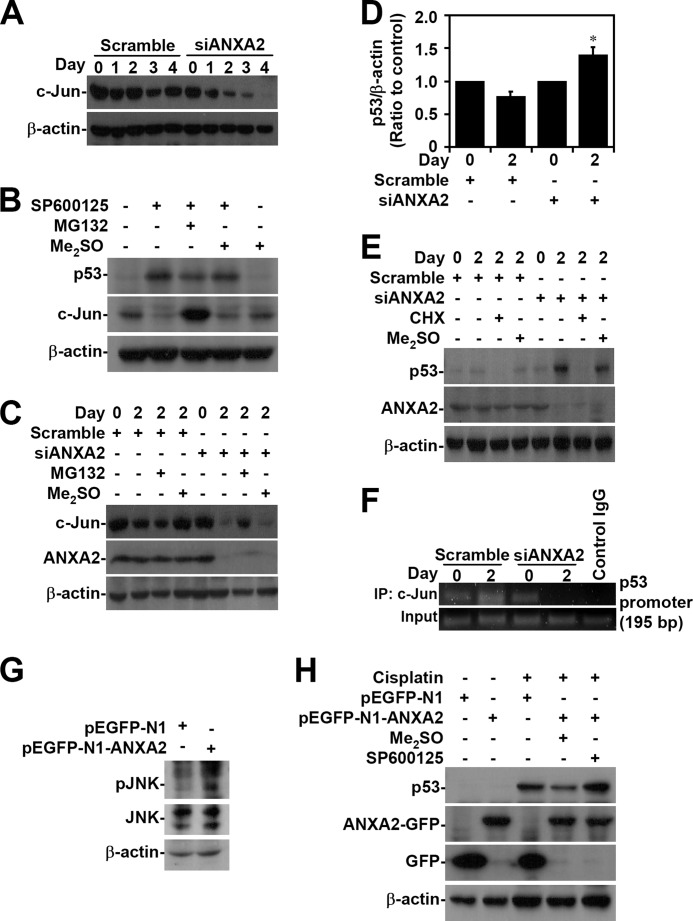
FIGURE 7.
ANXA2 deficiency causes JNK/c-Jun down-regulation, which causes the loss of transcriptional p53 suppression. A, ANXA2 was silenced with siANXA2 in A549 cells. Western blotting was used to determine the expression of c-Jun at the indicated times. A non-targeting siRNA (scramble) was used as a negative control. B, A549 cells were treated with the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (25 μm) in the absence or presence of the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (1.5 μm) for 24 h. Western blotting was used to determine the expression of p53 and c-Jun. C, ANXA2-deficient A549 cells were treated with MG132 for 48 h. Western blot analysis was used to detect the expression of c-Jun and ANXA2. DMSO and scrambled siRNA were used as negative controls. D, we performed real-time RT-PCR to determine the p53 mRNA expression in ANXA2-deficient A549 cells 2 days post-transfection. The data are shown as the mean -fold change ± S.D. (error bars) normalized to untreated cells grown in triplicate cultures. *, p < 0.05 compared with scramble. E, ANXA2-deficient A549 cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX; 5 μg/ml) for 48 h. Western blot analysis was used to detect the expression of p53 and ANXA2. DMSO and the scrambled siRNA were used as negative controls. F, chromatin immunoprecipitation was used to determine the binding capacity of c-Jun to p53 promoter in ANXA2-deficient A549 cells. The enrichment of the p53 promoter in immunoprecipitated (IP) c-Jun and the input of c-Jun are shown. IgG was used as a negative control. One representative data set of three individual experiments is shown. G, ANXA2 was overexpressed in A549 cells by pEGFP-N1-ANXA2 transfection. Western blotting showed the expression of phospho-JNK Thr-183/Tyr-185 (pJNK) and JNK. H, pEGFP-N1-ANXA2-transfected A549 cells were treated with cisplatin for 24 h. Western blotting showed the expression of p53 and ANXA2. pEGFP-N1 was used as a negative control. For Western blot analysis, β-actin was the internal control. The data shown are representative of three individual experiments.