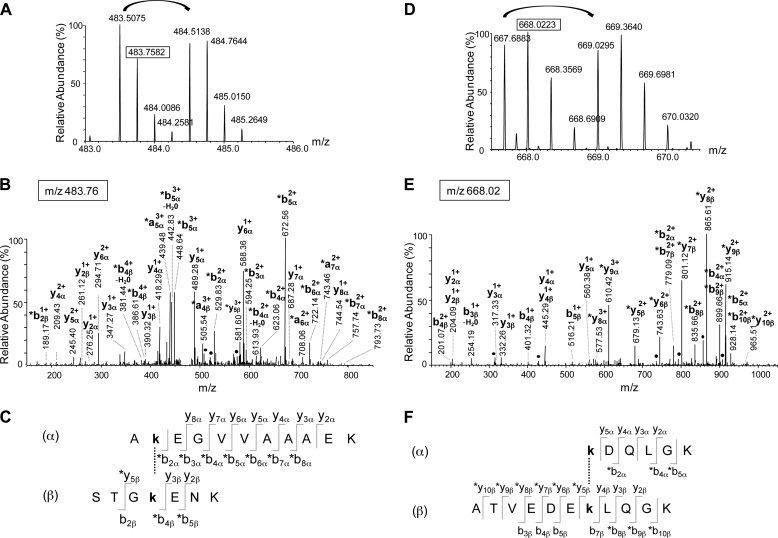
FIGURE 4.
Identification of two cross-links between α-Syn and Hsc70. A–C, identification of the cross-link between peptide 11–21 from α-Syn and peptide 494–500 from Hsc70. A, mass spectrum of the quadruple charged cross-linked peptide with m/z 483.5075 and 484.5138 for the BS2G-d0 and BS2G-d4 peptides respectively. B, fragmentation spectrum of the precursor ion at m/z 483.76 corresponding to the second isotope of the BS2G-d0 peptide. The identified fragments and their charge state are indicated. The asterisks indicate the fragments with the BS2G-d0 cross-linker. C, the identified fragments are indicated on the cross-linked sequences. The α- and β-sequences correspond to the 11–21 α-Syn and the 494–500 Hsc70 peptides, respectively. This cross-link involves residues Lys-12 and Lys-497 from α-Syn and Hsc70, respectively. D–F, identification of the cross-link between peptide 97–102 from α-Syn and peptide 551–561 from Hsc70. D, mass spectrum of the triple charged cross-linked peptide with m/z 667.6883 and 669.0295 for the BS2G-d0 and BS2G-d4 peptides, respectively. E, Fragmentation spectrum of the precursor ion at m/z 668.02 corresponding to the second isotope of the BS2G-d0 peptide. The identified fragments are indicated, together with their charge state. The asterisks indicate the fragments with the BS2G-d0 cross-linker. F, the identified fragments are indicated on the cross-linked sequences. The α- and β-sequences correspond to the 97–102 α-Syn and the 551–561 Hsc70 peptides, respectively. This cross-link involves residues Lys-97 and Lys-557 from α-Syn and Hsc70, respectively.