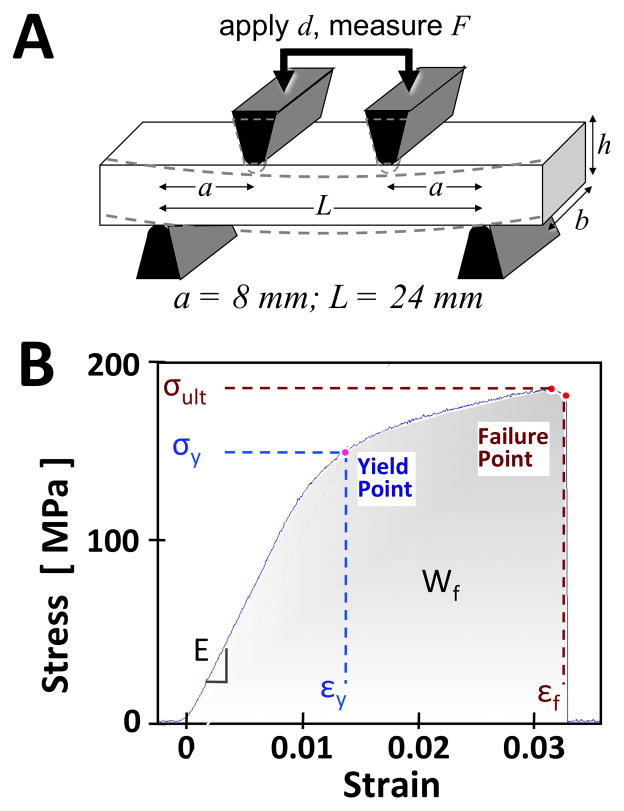
Figure 2.
Biomechanical testing device (A) and determination of properties from stress-strain data (B). In (A) the four-point bending test utilizes two loading jigs with a specific geometry (where a is the distance between inner and outer jigs, L is the width of outer jigs) compressing (to a depth of d) a rectangular sample (where b is the width and h is the height) while recording the force applied (F). Biomechanical measures were then obtained from the stress-strain curve (B). These included Young’s modulus (E), yield stress (σy), yield strain (εy), failure strain (εf), failure energy (Wf), and ultimate stress (σult).