Figure 7. CaCO3 precipitation assays I and II.
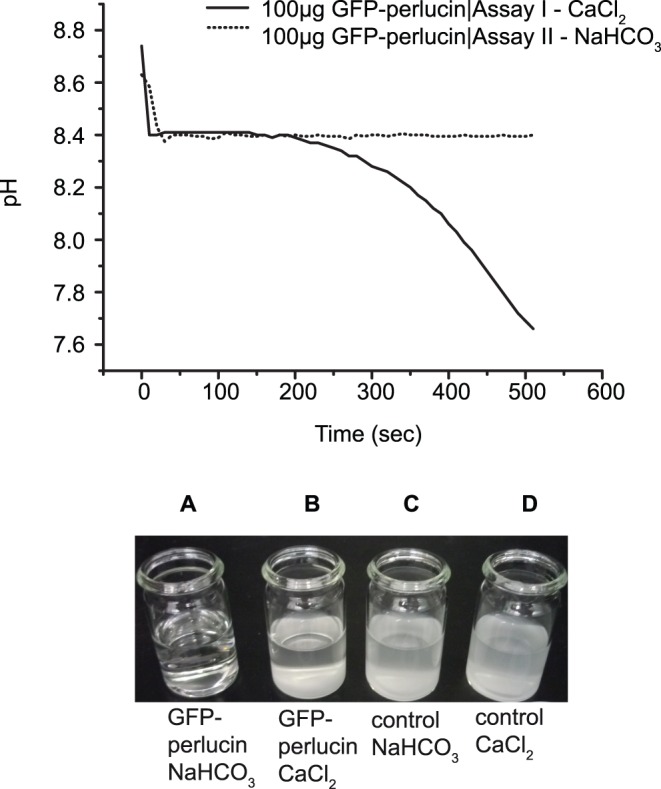
The inhibitory effect of high protein concentrations on the precipitation of calcium carbonate depends on the initial protein precursor solution. The presence of 25–100 µg GFP or GFP-perlucin in a NaHCO3 precursor solution delays the precipitation of calcium carbonate when Ca2+ is added to this solution (top, dotted line; bottom, vial A). A protein/CaCl2 precursor solution precipitates within ∼10 min from the addition of HCO3 – as indicated by the pH curve (top, solid line) and yields a white precipitate (bottom, vial B). While the time-course of the pH drop observed in control experiments without protein additives is similar to the protein/CaCl2 precursor, regardless of which one of the solutions is present in the vial and which one is added, the turbidity of the suspensions (bottom, vials C and D) differ from protein/CaCl2 precursors (bottom, vial B). The changes of pH values during the initial time intervals of precipitation are summarized in Table 2.
