Figure 5. The flagellum-attenuated Salmonella strains confer protective immunity against wt Salmonella challenge.
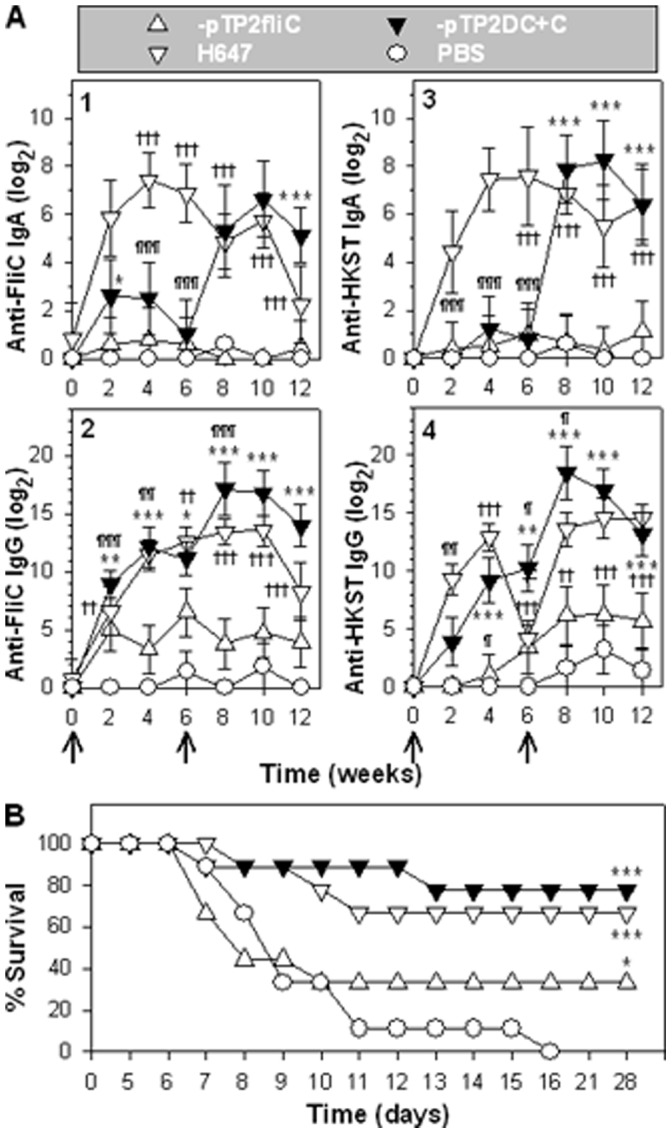
(A) ELISA titration of anti-FliC and anti-HKST Ab endpoint titers. BALB/c mice (4–5 individuals/group) were orally immunized with 1×109 CFU of P1-pTP2fliC, -pTP2DC+C, H647, and sPBS at weeks 0 and 6. The copro-IgA (1, 3) and serum IgG (2, 4) specific for FliC (1, 2) and HKST (3, 4) Ab titers were measured biweekly, and the significant differences are indicated: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 for P1-pTP2DC+C vs. -pTP2fliC; ¶ P<0.05, ¶¶ P<0.01, and ¶¶¶ P<0.001 for -pTP2DC+C vs. H647; and † P<0.05, †† P<0.01, and ††† P<0.001 for -pTP2fliC vs. H647. Each experiment was repeated twice, and depicted are the means ± SEM. (B) Protective efficacy assay. Immunized mice (A) were orally challenged with 5×107 CFUs of wt S. Typhimurium H71, and survival fractions obtained from P1-pTP2fliC (n = 9 mice), -pTP2DC+C (n = 9 mice), or H647-dosed mice (n = 9 mice) were compared with sPBS-dosed (n = 9 mice) mice and significances are indicated: ***P<0.001 for P1-pTP2DC+C, -pTP2fliC, or H647 vs. sPBS. The depicted are the mean of two independent experiments.
