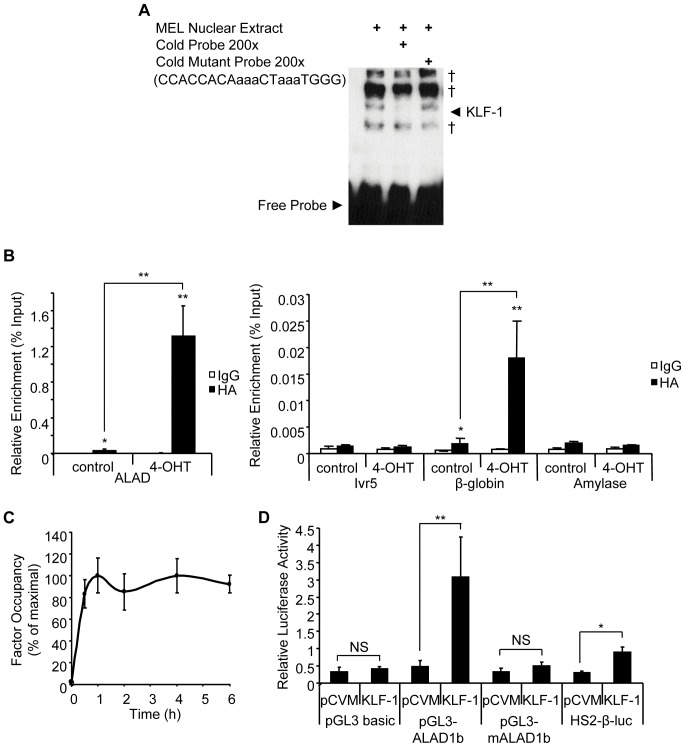
Figure 2. KLF1 binds at the Alad1b promoter in K1-ERp cells.
(A) EMSA using a probe specific for the CACC box of the Alad1b promoter. Binding specificity was confirmed with the use of a mutated probe. † represents non-specific signal. (B + C) ChIP performed chromatin derived from K1-ERp cells treated with either vehicle control or 4-OHT. An antibody specific to HA epitope tag was used. Target DNA enrichment relative to input was determined by Q-PCR. (B) Sequences used were Alad1b-specific encoding the CACC element, β-globin and amylase promoter-specific as positive and negative controls respectively. Ivr5 primers, located approximately 1 kb upstream of the β-globin promoter served as a control for sonication conditions. (C) Kinetic analysis of KLF1 occupancy at the Alad1b promoter relative to maximum detected occupancy as determined by ChIP performed on K1-ERp cells harvested at 0, 0.5, 1,2, 4 and 6 h into 4-OHT treatment. (D) Dual luciferase reporter assay performed in K562 cells in the presence of vector only or KLF1 expression vector. Mean relative luciferase levels were corrected to Renilla luciferase levels. HS2-β-luc construct contains the β-major CACC element and was used as a positive control. pGL3-mAlad1b corresponds to the Alad1b promoter sequence bearing mutations within the CACC element. *p value≤0.05. **p value ≤0.01 by Student’s t-test. Data shown represents the average of at least 3 independent experiments (mean ± SEM).