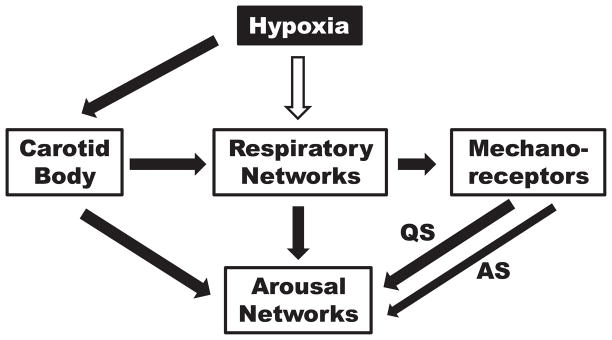
Figure 8.
Cartoon showing proposed contribution of carotid body chemoreceptors, respiratory networks and pulmonary or chest wall mechanoreceptors to arousal in response to hypoxia. The white arrow indicates inhibition and the black arrows excitation. During AS, there is a decreased contribution from mechanoreceptors indicated by the thinner arrow.