Fig. 1.
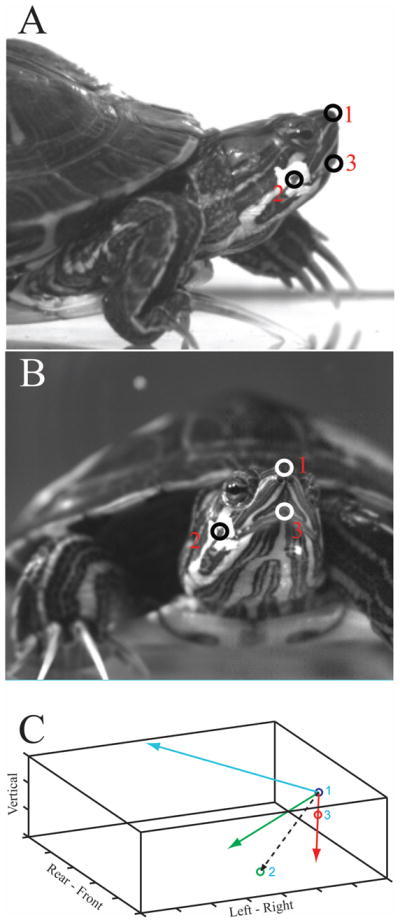
The three visible head landmarks that were tracked in the video sequences are seen in lateral (A) and frontal (B) views: the tip of the nose (1), the angle of the jaw (2), and the tip of the upper jaw (3). C. Construction of the body centered reference frame (B-frame) within the E-frame. The E-frame is represented by the tank in which the animal was filmed (solid black lines). Axis labels indicate direction when viewing the tank from the side; each division is 5mm. The B-frame is constructed from the plane containing the three skull landmarks. Point 1 is used as the origin of the B-frame, and a vector from point 1 to point 3 (red line) is the first in-plane axis. The vector cross-product between this axis and a vector from point 1 to point 2 (dashed black line) yields the B-frame axis (blue line) that is normal to the plane defined by the three skull landmarks. A vector cross-product between these two axes is used to form the second in-plane axis of the B-frame (green line).
