Figure 1.
Shutdown Is an Essential piRNA Pathway Factor
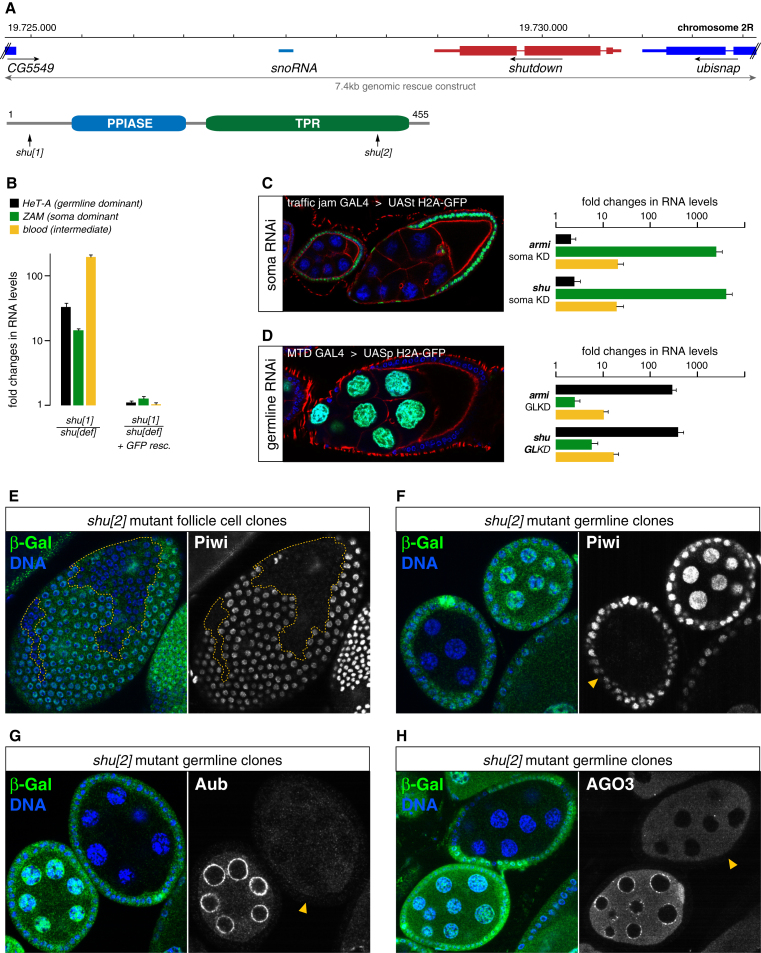
(A) Shown is the genomic shu locus, the extent of the rescue construct and the domain composition of the 455 amino acid Shu protein (arrows indicate the two nonsense mutations in shu[1] and shu[2]).
(B) Fold changes in steady state RNA levels of indicated TEs in shu mutant and GFP-shu-rescued ovaries (normalized to shu heterozygotes; n = 3; error bars indicate StDev.).
(C and D) Immunofluorescence images show soma (C) and germline (D) specificity of tj-Gal4 and MTD-Gal4 (crossed to UAS H2A-GFP (green); DNA (blue); actin (red)). Bar diagrams show fold changes in steady state RNA levels of indicated TEs upon soma (C) or germline (D) specific knockdown of armi or shu (n = 3; StDev.).
(E) Confocal section of a follicle epithelium with a mitotic shu[2] clone (marked by absence of β-Gal (green)) stained for DNA (blue) and Piwi (monochrome). The dashed yellow line marks the clone boundary.
(F–H) Confocal sections of two egg chambers with one being mutant for shu[2] in the germline (absence of β-Gal (green); yellow arrowhead in monochrome panels) stained for DNA (blue), Piwi (F), Aub (G) or AGO3 (H).