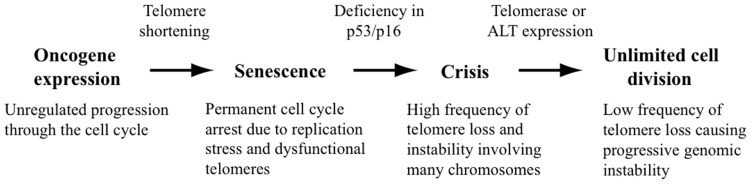
FIGURE 1.
Contribution of telomere loss to chromosome instability in cancer. Oncogene expression causes unregulated cell division, resulting in replication stress and excessive telomere shortening. The very short telomeres or DSBs near telomeres that are caused by replication stress result in cell senescence. Mutations in the p53 and p16 proteins that are required for cell cycle regulation can allow cells to continue to divide, leading to cell crisis as a result of dysfunctional telomeres and extensive chromosome fusion. The activation of telomerase expression or the ALT pathway in rare cells allows for continued cell division, although the surviving cells will contain chromosome rearrangements as a result of telomere loss during crisis. Cells expressing telomerase will continue to experience a low rate of telomere loss due to a combination of replication stress causing DSBs near telomeres and a deficiency in DSB repair in subtelomeric regions.