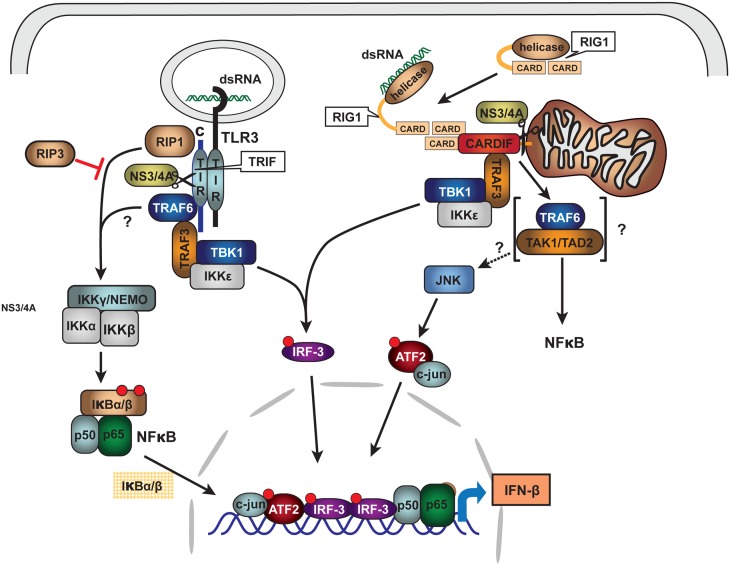
Figure 5.
Schematic of HCV NS3/4A protease inhibition of innate immune signaling pathways: TLR3 and RIG1. Double stranded RNA (dsRNA) viruses or viruses with dsRNA intermediate activate innate immune system signaling pathways for type I interferon induction through binding to Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRR). For HCV, PRR are associated with at least two major signaling pathways: TLR3 and RIG1. Upon intracellular binding of dsRNA to associated adapter proteins TRIF and CARDIFF, respectively, signaling is transmitted through complex intermediate steps of recognition, binding, and phosphorylation leading to activation of the transcriptional factors IRF3 and NFκB. The activated nuclear transcription factors bind to type I interferon promoters and induce α/β-interferon transcription. HCV NS3/4A protease is known to cleave both TRIF and CARDIFF adapters thus crippling innate immune antigen recognition and signaling for type I interferon induction. With permission (Bode et al., 2007), see original review for terminology and abbreviations.