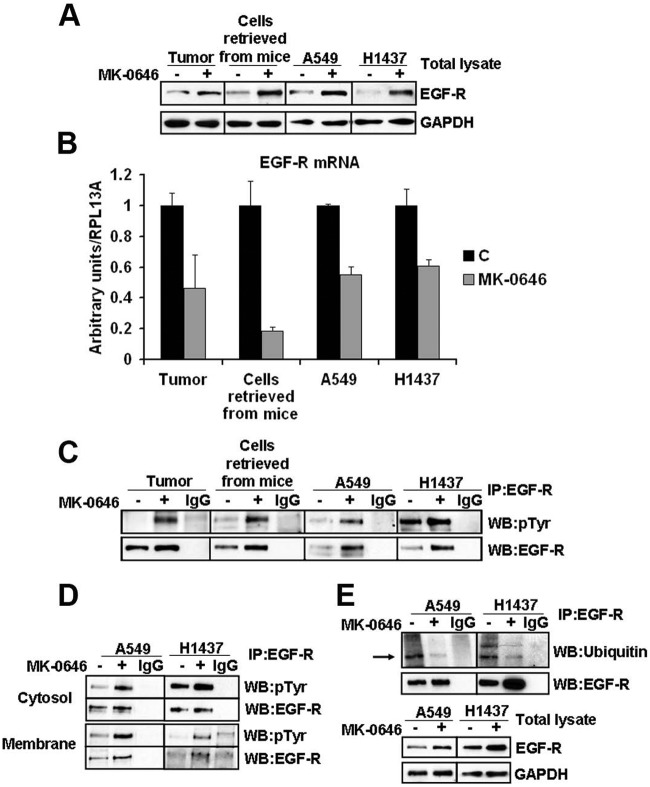
Figure 4.
Increased expression and activation of EGF-R in MK-0646 treated cells both in vivo and in vitro. (A) Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins in 2 representative protein lysates obtained from the postcaval lung lobe of a control and MK-0646 treated mice, in 3 pooled cell lines re-derived after necroscopy from lung tumors of control mice and mice treated with MK-0646, in A549 and H1437 cells treated either with an irrelevant human IgG or with MK-0646 for 3 weeks. (B) RT-Q-PCR of the EGF-R mRNA measured from the sources specified in (A). Columns represent the average of 4 independent experiments; bars represent standard deviation. (C) Immunoprecipitation of the EGF-R from the sources specified in (A) followed by immunoblot analysis using the specified antibodies. IgG lanes: immunoprecipitation performed using a pre-immune mouse IgG (negative control). (D) Biotinylation of cell-surface proteins; streptavidin pull-down followed by EGF-R immunocapture (see Materials and Methods for details) and Western blot analysis performed using the indicated antibodies. Note increased EGF-R phosphorylation both in plasma membrane proteins (Membrane) and in proteins not present at the plasma membrane (Cytosol), while the expression level of EGF-R protein appears elevated only in the plasma membrane fraction. IgG lanes: EGF-R immunoprecipitation performed using a pre-immune mouse IgG (negative control) (E) EGF-R immunoprecipitation followed by Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. IgG lanes: same as in (C) and (D).