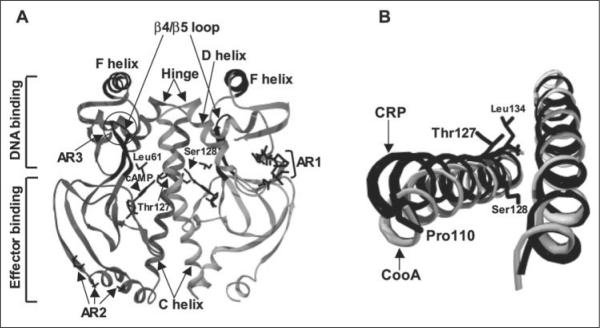
FIGURE 1.
A, shown is the structure of active cAMP-bound E. coli CRP (Protein Data Bank code 1CGP). CRP is composed of a homodimer with an interface along the long C-helices. The bound cAMP molecules and residues Thr127, Ser128, and Leu61 are visible in the center of this figure and are labeled in one monomer. The C-helices, D-helices, hinge regions, and β4/β5 loops are indicated by arrows. The F-helices are responsible for DNA binding. The ARs involved in the interaction with RNA polymerase (AR1, AR2, and AR3) are also indicated. B, the relative C-helix positions are different between active CRP (black) and inactive CooA (gray) when one of the two C-helices in each protein is aligned (right). The effector-free inactive CooA structure is from the Protein Data Bank (code 1FT9). This view is from effector-binding domains toward DNA-binding domains. Both figures were generated using Swiss-PdbViewer Version 3.7.