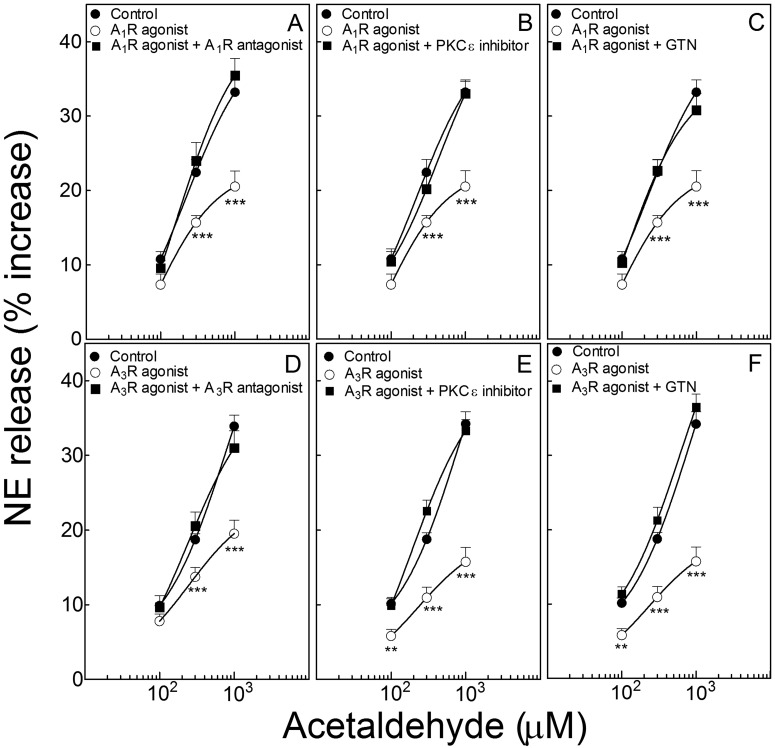
Fig. 3.
Activation of adenosine A1 and A3 receptors inhibits the acetaldehyde-induced NE release from isolated cardiac synaptosomes: prevention by either PKCε inhibition or ALDH2 desensitization. Points (means ± S.E.M.; n = 8–42) represent percentage increases in NE release above a mean basal control level of 267 ± 6.6 pmol/mg protein (n = 124). A, selective activation of A1 receptors with 2′-MeCCPA (10 nM; 10 min) attenuates NE release by acetaldehyde, an action that is prevented by A1-receptor blockade with DPCPX (300 nM; 10 min). B and C, the A1 receptor-induced attenuation of NE release is prevented either by PKCε inhibition with εV1–2 (1 μM; 10 min) (B) or ALDH2 desensitization with GTN (2 μM; 30 min) (C). D, selective activation of A3 receptors with IB-MECA (50 nM; 10 min) attenuates NE release by acetaldehyde, an action that is prevented by A3-receptor blockade with MRS1523 (100 nM; 10 min). E and F, the A3 receptor-induced attenuation of NE release is prevented either by PKCε inhibition with εV1–2 (1 μM; 10 min) (E) or ALDH2 desensitization with GTN (2 μM; 30 min) (F). **, P < 0.01 and ***, P < 0.001 from control and A1- and A3-receptor agonists in combination with respective antagonists or in combination with εV1–2 or GTN, by unpaired t test.